New FAQ Page 2 - ఆర్బిఐ - Reserve Bank of India
 IST,
IST,
FAQs on Resolution Framework for Covid-19 related stress (Revised on December 12, 2020) (Updated as on August 19, 2022)
For the borrowers eligible for resolution under the circular dated August 6, 2020 on Resolution Framework for COVID-19-related Stress, the circular dated August 6, 2020 will be applicable if a resolution process under the circular is invoked. For all other borrowers, the extant instructions as otherwise applicable shall still be in force. However, if any entity is otherwise eligible to be resolved under the Resolution Framework, only Resolution Framework can be used for resolving the stress arising out of the pandemic.
All loans meeting the eligibility criteria, unless covered by the specific exclusions listed in Paragraph 2 of the Annex to the Resolution Framework subject to the clarification at Sl. No. 2 above fall within the scope of resolution under the framework. These loans, if not falling under any of the categories mentioned in Paragraph 2 of the Annex to the Resolution Framework, is eligible for resolution under Part A of the Annex if they fall within the purview of “personal loans” as defined in the Circular DBR.No.BP.BC.99/08.13.100/2017-18 dated January 4, 2018 on “XBRL Returns – Harmonization of Banking Statistics”, even if they are not explicitly classified as so in any regulatory / supervisory reporting, or under Part B of the Annex otherwise.
Members of the public may approach bank branches for deposit and/or exchange of ₹2000 banknotes held by them.
The facility for deposit into accounts and exchange for ₹2000 banknotes will be available at all banks until September 30, 2023. The facility for exchange will be available also at the 19 Regional Offices (ROs) of RBI having Issue Departments1 until September 30, 2023.
Ans. Yes, for providing a non-microfinance loan to a low-income household (as defined under the directions), it should be ensured that the limit of 50 per cent on monthly loan repayment obligations of a household as a percentage of monthly household income is not breached. In other words, the limit of 50 per cent shall include both microfinance as well as non-microfinance loans.
Answer: This is essentially a bank-to-bank arrangement similar to correspondent banking arrangement.
Ans. Yes. Under this facility, cash can be withdrawn from PoS terminal(s) at designated merchant establishment(s), irrespective of the fact whether the card issuer and the acquiring bank are same or not.
Ans. Yes provided the bank account is re-designated as a BO account.
- Interest will be accrued and compounded in the principal on half-yearly basis and paid along with principal at the time of redemption.
Ans. Direct participation in CPS can reduce delay in execution of funds transfer instructions of non-banks. Further, if there is any impact in the functioning of the bank, it can cause business disruptions for its non-bank customers as well. Such disruptions, even if temporary, can have the potential to spread instability in the system.
Direct participation to CPS will enable access neutrality between banks and non-banks and facilitate better settlement risk management with increased participation of non-banks.
-
There is no bar on processing of payment transactions outside India if so desired by the PSOs. However, the data shall be stored only in India after the processing. The complete end-to-end transaction details should be part of the data.
-
In case the processing is done abroad, the data should be deleted from the systems abroad and brought back to India not later than the one business day or 24 hours from payment processing, whichever is earlier. The same should be stored only in India.
-
However, any subsequent activity such as settlement processing after payment processing, if done outside India, shall also be undertaken / performed on a near real time basis. The data should be stored only in India.
In case of any other related processing activity, such as chargeback, etc., the data can be accessed, at any time, from India where it is stored.
Ans. Banks, NBFC - Factors and other financial institutions as permitted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), can participate as financiers in TReDS.
SNRR A/c can be used for transactions as permitted under A.P.(DIR Series) Circular No.09 dated November 22, 2019. These transactions should be carried out only if recording and reporting of such transactions under FETERS can be undertaken apart from other FEMA compliances. It may be noted that the transactions under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) are not permitted to be routed through the SNRR account.
For redressal of grievance, the complainant must first approach the concerned NBFC. If the NBFC does not reply within a period of one month after receipt of the complaint, or the NBFC rejects the complaint, or if the complainant is not satisfied with the reply given by the NBFC, the complainant can file the complaint with the NBFC Ombudsman under whose jurisdiction the branch/ registered office of the NBFC falls.
-
A first time user should register through ATS using his/her valid email id.
-
A system generated Password will be forwarded to the applicant’s email id.
-
Thereafter, the applicant can login and submit his/her application and track the same.
-
As soon as an application is submitted through ATS, a unique application number is generated and forwarded to the applicant by the system.
-
A mail is sent by the system automatically when the application is disposed of or transferred from one office / department / section to another.
Answer: RBI approval is required if:
(i) Remittance is in excess of USD 1,000,000 (US Dollar One million only) per financial year:
- on account of legacy, bequest or inheritance to a citizen of foreign state, resident outside India; and
- by NRIs/ PIOs out of the balances held in NRO accounts/ sale proceeds of assets/ the assets acquired by way of inheritance/ legacy.
(ii) Hardship will be caused to a person if remittance from India is not made to such a person.
CTS enables fast and cheap realisation of funds to customers as compared to traditional mechanisms. Under grid-based CTS clearing, all cheques drawn on bank branches falling within in the grid jurisdiction are treated and cleared as local cheques. No outstation cheque collection charges to be levied if the collecting bank and the paying bank are located within the jurisdiction of the same CTS grid even though they are located in different cities.
CTS also benefits issuers of cheques. The Corporates if needed can be provided with images of cheques by their bankers for internal requirements, if any.
Ans : The User intending to effect payments through ECS Credit has to submit details of the beneficiaries (like name, bank / branch / account number of the beneficiary, MICR code of the destination bank branch, etc.), date on which credit is to be afforded to the beneficiaries, etc., in a specified format (called the input file) through its sponsor bank to one of the ECS Centres where it is registered as a User.
The bank managing the ECS Centre then debits the account of the sponsor bank on the scheduled settlement day and credits the accounts of the destination banks, for onward credit to the accounts of the ultimate beneficiaries with the destination bank branches.
Further details about the ECS Credit scheme are contained in the Procedural Guidelines and available on the website of Reserve Bank of India at http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/ECSUserView.aspx?Id=1
Answer: An NRO (current/ savings) account can be opened by a foreign national of non-Indian origin visiting India, with funds remitted from outside India through banking channel or by sale of foreign exchange brought by him to India. The balance in the NRO account may be paid to the account holder at the time of his departure from India provided the account has been maintained for a period not exceeding six months and the account has not been credited with any local funds, other than interest accrued thereon.
Ans: Bank-wise list of IFSCs is available with all the bank-branches participating in NEFT scheme. List of bank-wise branches participating in NEFT and their IFSCs is also available on the website of RBI at /en/web/rbi/-/list-of-neft-enabled-bank-branches-bank-wise-indian-financial-system-code-updated-as-on-june-30-2023-2009-1. All member banks have also been advised to print the IFSC of the branch on cheques issued to their customers.
Application in the prescribed form (as given in Part I: Annex-I of the FED Master Direction No.18/2015-16 on Reporting under FEMA 1999), along with the required documents should be submitted to the respective Regional Office of the Foreign Exchange Department of the Reserve Bank under whose jurisdiction the registered office of the applicant company falls.
Ans. A person coming into India from abroad can bring with him foreign exchange without any limit. However, if the aggregate value of the foreign exchange in the form of currency notes, bank notes or travellers cheques brought in exceeds USD 10,000 or its equivalent and/or the value of foreign currency alone exceeds USD 5,000 or its equivalent, it should be declared to the Customs Authorities at the Airport in the Currency Declaration Form (CDF), on arrival in India.
Like in most countries, banks in India also are required to develop their own individual policy / procedures relating to collection of cheques. The customer is entitled to receive due disclosures from the bank on the bank's obligations and the customers' rights.
Broadly, the policies formulated by banks should cover the following areas:
Immediate credit for local / outstation cheques, Time frame for collection of local / outstation instruments and compensation payable for delayed collection.
The CCPs of various banks are made available on the website of respective bank.
Banks are obliged to disclose their liability to customers by way of compensation / interest payments due to delays for non-compliance with the standards set by the banks themselves. The customer has to be compensated by way of compensation/interest payment even if no formal claim is lodged to the effect.
Application for the deposit will be available at branches of Authorised Banks. It is also available in the Reserve Bank of India website.
Response: The deposit under STBD (1-3 years), MTGD (5-7 years), and LTGD (12-15 years) can be made for only specified timeframe. These deposits can be subsequently renewed upon maturity.
Response
No. An individual is eligible to have only one 'Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account' in one bank.
Yes. One can have Term/Fixed Deposit, Recurring Deposit etc., accounts in the bank where one holds 'Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account'.
Ans: The applicant should give the list of promoters and the source of funds for the minimum capital of Rs 2 crore. The capital should be infused before issue of CoR. No change in promoters will be allowed in the interregnum.
On behalf of GAH, PM needs to submit an access request form to CCIL. The Request would be formally addressed to RBI. However, CCIL has been authorized to directly receive and process Access Request Form from PM for operational convenience. A detailed operation flow is contained in Annexure I.
Ans : NBFCs desirous of sponsoring IDF-MFs are required to comply with the following requirements :
-
The NBFC should have a minimum Net Owned Funds (NOF) of Rs.300 crore; and Capital to Risk Weighted Assets (CRAR) of 15%;
-
its net NPAs should be less than 3% of net advances;
-
it should have been in existence for at least 5 years;
-
it should be earning profits for the last three years and its performance should be satisfactory;
-
the CRAR of the NBFC post investment in the IDF-MF should not be less than the regulatory minimum prescribed for it;
-
The NBFC should continue to maintain the required level of NOF after accounting for investment in the proposed IDF and
-
There should be no supervisory concerns with respect to the NBFC.
Answer: A resident individual can open a foreign currency account with a bank outside India in the following cases:
1) A resident student who has gone abroad for studies for the period of stay abroad. All credits to the account from India should be made in accordance with FEMA and the rules and regulations made thereunder. On the student’s return to India after completion of studies, the account will be deemed to have been opened under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme (LRS).
2) A resident who is on a visit to a foreign country for the period of stay abroad. The balance in the account should be repatriated to India on return of the account holder to India.
3) A person going abroad to participate in an exhibition/ trade fair for crediting the sale proceeds of goods. The balance should be repatriated to India within one month from the date of closure of the exhibition/ trade fair.
4) The following persons for remitting/ receiving their entire salary payable to them in India:
-
A foreign citizen resident in India, who is an employee of a foreign company and is on deputation to the office/ branch/ subsidiary/ joint venture/ group company in India;
-
An Indian citizen who is an employee of a foreign company and is on deputation to the office/ branch/ subsidiary/ joint venture/ group company in India; and
-
A foreign citizen who is a resident in India and is employed with an Indian company.
5) For the purpose of sending remittances under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme.
Ans. Yes. The application in the prescribed format along with necessary documents and a demand draft for Rs. 5000/- (Rupees five thousand only) drawn in favour of the “Reserve Bank of India” should be sent to the Reserve Bank of India while sending the request for compounding.
-
Index ratio (IR) will be calculated by dividing the reference WPI on the settlement date with the reference WPI on the issue date.
-
The formula for the same is as under:
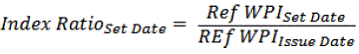
Any clarification in respect of specific cases could be obtained from the Reserve Bank’s Central office at the following address:
Overseas Investment Division,
Exchange Control Department,
Central office,
Reserve Bank of India,
Mumbai 400001.
or
e-mail: oid@rbi.org.in
Banks generally offer either of the following loan options: Floating Rate Home Loans and Fixed Rate Home Loans. For a Fixed Rate Loan, the rate of interest is fixed either for the entire tenure of the loan or a certain part of the tenure of the loan. In case of a pure fixed loan, the EMI due to the bank remains constant. If a bank offers a Loan which is fixed only for a certain period of the tenure of the loan, please try to elicit information from the bank whether the rates may be raised after the period (reset clause). You may try to negotiate a lock-in that should include the rate that you have agreed upon initially and the period the lock-in lasts.
Hence, the EMI of a fixed rate loan is known in advance. This is the cash outflow that can be planned for at the outset of the loan. If the inflation and the interest rate in the economy move up over the years, a fixed EMI is attractively stagnant and is easier to plan for. However, if you have fixed EMI, any reduction in interest rates in the market, will not benefit you.
Determinants of floating rate:
The EMI of a floating rate loan changes with changes in market interest rates. If market rates increase, your repayment increases. When rates fall, your dues also fall. The floating interest rate is made up of two parts: the index and the spread. The index is a measure of interest rates generally (based on say, government securities prices), and the spread is an extra amount that the banker adds to cover credit risk, profit mark-up etc. The amount of the spread may differ from one lender to another, but it is usually constant over the life of the loan. If the index rate moves up, so does your interest rate in most circumstances and you will have to pay a higher EMI. Conversely, if the interest rate moves down, your EMI amount should be lower.
Also, sometimes banks make some adjustments so that your EMI remains constant. In such cases, when a lender increases the floating interest rate, the tenure of the loan is increased (and EMI kept constant).
Some lenders also base their floating rates on their Benchmark Prime Lending Rates (BPLR). You should ask what index will be used for setting the floating rate, how it has generally fluctuated in the past, and where it is published/disclosed. However, the past fluctuation of any index is not a guarantee for its future behavior.
Flexibility in EMI:
Some banks also offer their customers flexible repayment options. Here the EMIs are unequal. In step-up loans, the EMI is low initially and increases as years roll by (balloon repayment). In step-down loans, EMI is high initially and decreases as years roll by.
Step-up option is convenient for borrowers who are in the beginning of their careers. Step-down loan option is useful for borrowers who are close to their retirement years and currently make good money.
Ans: Bonds subscribed by banks and which meet the criteria specified in circular dated April 23, 2010 will continue to be classified under HTM category.
సమాధానం. నగదు సరఫరా చేయడానికి అదనంగా, ఎటిఎంలు/ డబ్ల్యు.ఎల్.ఎలు కస్టమర్లకు అనేక ఇతర సేవలు /సదుపాయాలు అందిస్తాయి. ఈ సేవలలో కొన్ని:
- అకౌంట్ సమాచారం
- నగదు జమ (డబ్ల్యు.ఎల్.ఎలలో అనుమతించబడదు)
- సాధారణ బిల్లుల చెల్లింపు (డబ్ల్యు.ఎల్.ఎలలో అనుమతించబడదు)
- మొబైల్స్ కి రీ-లోడ్ ఓచర్లను కొనడం (డబ్ల్యు.ఎల్.ఎలలో అనుమతించబడదు)
- మినీ/షార్ట్ స్టేట్మెంట్ పొందవచ్చు
- పిన్ మార్పు
- చెక్కు బుక్ కోసం అభ్యర్థన
సమాధానం. ఎన్.ఇ.ఎఫ్.టి అనేది ఎలక్ట్రానిక్ ఫండ్ ట్రాన్స్ ఫర్ సిస్టమ్. దీనిలో నిర్దిష్ట సమయం వరకు అందిన లావాదేవీలను అన్నీ కలిపి ఒకసారి ప్రాసెస్ చేస్తారు. దీనికి భిన్నంగా, ఆర్.టి.జి.ఎస్.లో ఆర్.టి.జి.ఎస్ వ్యాపార వేళల అంతటా ఒకదాని తరువాత మరొక లావాదేవీ ప్రాతిపదికన, నిరంతరం లావాదేవీలను ప్రాసెస్ చేస్తారు.
All loans meeting the eligibility criteria, unless covered by the specific exclusions listed in Paragraph 2 of the Annex to the Resolution Framework subject to the clarification at Sl. No. 2 above fall within the scope of resolution under the framework. These loans, if not falling under any of the categories mentioned in Paragraph 2 of the Annex to the Resolution Framework, is eligible for resolution under Part A of the Annex if they fall within the purview of “personal loans” as defined in the Circular DBR.No.BP.BC.99/08.13.100/2017-18 dated January 4, 2018 on “XBRL Returns – Harmonization of Banking Statistics”, even if they are not explicitly classified as so in any regulatory / supervisory reporting, or under Part B of the Annex otherwise.
Ans. Non-banks increasingly and actively offer financial services and direct access to CPS can enable them to leverage technology and offer more choices to their consumers.
Apart from managing settlement risk in payments landscape, expanding access and participation of non-banks is a progressive move and leads to diversity and resiliency of the payments ecosystem.
Ans: No.
Answer: The AD bank approaching RBI for seeking approval for opening of Special Rupee Vostro Account must submit the following information along with their proposal/request:
-
The details of the arrangement between AD bank and correspondent bank from the trading partner country along with the funds flow.
-
A brief write-up on the foreign banks seeking correspondent relationship for Special Rupee Vostro Account.
-
Copy of the request letter of the correspondent bank to AD bank.
-
Confirmation from AD bank that the due diligence has been carried out by AD bank which establishes correspondent banking relationship as per our extant guidelines {Master Direction - Know Your Customer (KYC) Direction, 2016 dated Feb 25, 2016) (As amended from time to time)}.
-
Confirmation from AD bank stating that the correspondent bank is not from a country or jurisdiction in the updated FATF Public Statement on High Risk & Non-Co-operative jurisdictions on which FATF has called for counter measures.
-
Confirmation from AD bank that they shall ensure that all the transactions taking place in the Special Rupee Vostro Account of the correspondent bank are strictly in adherence to the instructions given in the A.P. (DIR Series) Circular No. 10 dated July 11, 2022.
-
Financial parameters pertaining to the correspondent bank as required for the proposal may be obtained beforehand by email to fedcotrade@rbi.org.in and the same may be furnished by AD bank along with the proposal.
Ans. Yes, the AD bank should ensure compliance to the extant instructions issued by the Department of Banking Regulation.
Ans. Broadly, following steps take place during financing / discounting through TReDS:
-
Creation of a Factoring Unit (FU) - standard nomenclature used in TReDS for invoice(s) or bill(s) of exchange - containing details of invoices / bills of exchange (evidencing sale of goods / services by the MSME sellers to the buyers) on TReDS platform by the MSME seller (in case of factoring) or the buyer (in case of reverse factoring);
-
Acceptance of the FU by the counterparty - buyer or the seller, as the case may be;
-
Bidding by financiers;
-
Selection of best bid by the seller or the buyer, as the case may be;
-
Payment made by the financier (of the selected bid) to the MSME seller at the agreed rate of financing / discounting;
-
Payment by the buyer to the financier on the due date.
Ans. No. The facility is available irrespective of whether the card holder makes a purchase or not.
- On redemption, investors will get principal and compounded interest.
Answer: A person resident in India may maintain a foreign currency account outside India if he had opened it when he was resident outside India or inherited it from a person resident outside India.
Ans. Board-approved policies of REs should cover such operational aspects. One possible way could be to distribute the annualized repayment obligations over twelve months to estimate monthly outgo of the household towards debt repayment.
Ans: Individuals, firms and corporates maintaining accounts with any member bank, participating in the NEFT system, can electronically transfer funds to any individual, firm or corporate having an account with any other bank in the country participating in the NEFT system.
The list of bank-wise branches participating in NEFT is available on the website of RBI at /en/web/rbi/-/list-of-neft-enabled-bank-branches-bank-wise-indian-financial-system-code-updated-as-on-june-30-2023-2009-1.
Ans. Foreign exchange for travel abroad can be purchased from an authorized person against rupee payment in cash below Rs.50,000/-. However, if the sale of foreign exchange is for the amount equivalent to Rs 50,000/- and above, the entire payment should be made by way of a crossed cheque/ banker’s cheque/ pay order/ demand draft/ debit card / credit card / prepaid card only.
Ans. All remittances are subject to payment of taxes as applicable in India – Authorised Dealers are to convince themselves on this aspect.
పేజీ చివరిగా అప్డేట్ చేయబడిన తేదీ: null
పేజీ చివరిగా అప్డేట్ చేయబడిన తేదీ: null











