Guidelines - ಆರ್ಬಿಐ - Reserve Bank of India
 IST,
IST,
Guidelines for the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS)
| Guidelines for the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) |
|---|
|
(Updated as on July 2, 2018) Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), despite the important role played by them in the economic fabric of the country, continue to face constraints in obtaining adequate finance, particularly in terms of their ability to convert their trade receivables into liquid funds. In order to address this pan-India issue through setting up of an institutional mechanism for financing trade receivables, the Reserve Bank of India had published a concept paper on “Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) Factoring-Trade Receivables Exchange” in March 2014. 2. Based on the public comments received on the concept paper and the subsequent draft guidelines issued for setting up and operating the system, and interactions held with relevant stakeholders, the following guidelines are being issued for setting up and operating the trade receivables system in the country. These Guidelines are issued by Reserve Bank of India under Section 10(2) read with Section 18 of Payment & Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (Act 51 of 2007). Scheme 3. The scheme for setting up and operating the institutional mechanism for facilitating the financing of trade receivables of MSMEs from corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), through multiple financiers will be known as Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS). 4. The TReDS will facilitate the discounting of both invoices as well as bills of exchange. Further, as the underlying entities are the same (MSMEs and corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and PSUs), the TReDS could deal with both receivables factoring as well as reverse factoring so that higher transaction volumes come into the system and facilitate better pricing. 5. The transactions processed under TReDS will be “without recourse” to the MSMEs. Definitions 6. For the purpose of the Scheme, notwithstanding any other definition used in any other context, scheme, law or document, the following definitions are used: a) Factoring unit - a standard nomenclature used in the TReDS for an invoice or a bill on the system. Factoring Units may be created either by the MSME seller (in the case of factoring) or by corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and PSUs, (in case of reverse factoring) as the case may be. b) Financier – refers to banks, NBFC Factors and other financial institutions as permitted by the Reserve Bank of India participating in the TReDS and accepting the factoring unit for financing purpose. Participants 7. MSME sellers, corporate and other buyers, including the Government Departments and PSUs, and financiers (banks, NBFC Factors and other financial institutions as permitted by the Reserve Bank of India) will be direct participants in the TReDS. The TReDS will provide the platform to bring these participants together for facilitating uploading, accepting, discounting, trading and settlement of the invoices / bills of MSMEs. The bankers of sellers and buyers may be provided access to the system, where necessary, for obtaining information on the portfolio of discounted invoices / bills of respective clients. The TReDS may tie up with necessary technology providers, system integrators and entities providing dematerialisation services for providing its services. Process flow and procedure 8. The objective of the TReDS is to facilitate financing of invoices / bills of MSMEs drawn on corporate and other buyers, including the Government Departments and PSUs, by way of discounting by financiers. To enable this, the TReDS has to put in place suitable mechanism whereby the invoice / bill is converted into “factoring unit” as indicated in the Annex. 9. In the first phase, the TReDS would facilitate the discounting of these factoring units by the financiers resulting in flow of funds to the MSME with final payment of the factoring unit being made by the buyer to the financier on due date. In the second phase, the TReDS would enable further discounting / re-discounting of the discounted factoring units by the financiers, thus resulting in its assignment in favour of other financiers. 10. The process flow of the TReDS has to enable at the minimum, the uploading of invoices/bills and creation of factoring units by the MSME sellers; its acceptance by the corporate and other buyers, including the Government Departments and PSUs, within a specified time limit; discounting, rating and re-discounting of factoring units; sending of notifications at each stage to the relevant parties to the transaction; reporting and MIS requirements; and finally, generation and submission of settlement of obligations. In case of reverse factoring, the buyer could also create factoring units based on the documents uploaded by the MSME seller. A brief illustrative outline of the minimum features required in the process flow is given in the Annex. 11. The actual business, technical and operational processes and procedures to be followed in the system will be prepared by the entity operating the TReDS, and will be part of the Procedural Guidelines for the system. 12. The TReDS may also undertake some random audits to ensure that the factoring units uploaded on the exchange are authentic & based on genuine underlying transactions involving the sale of goods or services. 13. TReDS would put in place a standardized mechanism / process for on-boarding of buyers and sellers on the TReDS. This one-time on-boarding process will require the entities to submit all KYC related documents to the TReDS, along with resolutions / documents specific to authorised personnel of the buyer, and the MSME seller. Such authorised personnel would be provided with IDs / Passwords for TReDS authorisations (multi-level). Indemnity in favour of TReDS, if required, may also be given if it is made part of the standardized on-boarding process. 14. The KYC documentation and its process may be standardised and disclosed to all stakeholders by TReDS. As it requires confirmation of the banker of the MSME seller / buyer, as the case may be, the KYC documentation may be synchronous with the documentation / verification done by the banks in adherence to the extant regulatory requirements (Reserve Bank of India’s “Master Direction - Know Your Customer (KYC) Direction, 2016” dated February 25, 2016 (as amended from time to time)). 15. There would be a one-time agreement drawn up amongst the participants in the TReDS: a) Master agreement between the financier and the TReDS, stating the terms and conditions of dealings between both the entities. b) Master agreement between the buyers and the TReDS, stating the terms and conditions of dealings between both the entities. This agreement should clearly capture the following aspects:
c) Master agreement between the MSME sellers and the TReDS, stating the terms and conditions of dealings between both the entities. The agreement should also have a declaration / undertaking by the MSME seller that, in respect of goods and services underlying the factoring unit, no finance is extended by the working capital financing bank and such goods and services are not charged to the working capital financing bankers (i.e., finance availed through the TReDS would not be part of existing charge / hypothecation of its working capital bankers). d) In case of financing on the basis of invoices, an assignment agreement would need to be executed between the MSME seller and the financier. Alternatively, this aspect may be incorporated in the agreement between the MSME seller and the financier, to the effect that any financing transaction on TReDS will tantamount to an assignment of receivables in favour of whoever is the financier. e) The TReDS will be in custody of all the agreements. 16. Other procedural aspects of TReDS functioning and operations may be incorporated either in the Master Agreement, if so necessitated by the participants, or in the Procedural Guidelines where applicable. In all instances, such procedural aspects, even if incorporated in the Master Agreements, should be in adherence to regulatory norms issued from time to time. The Master Agreement may also clearly indicate that any legal proceedings to be initiated by one entity against another, if at all, will be outside the purview of TReDS. 17. TReDS will also review the need for CERSAI registration for the assignments as indicated above, and put in place a suitable mechanism for the same (preferably driven automatically through the TReDS), as soon as feasible after a factoring unit has been accepted for financing by a financier. Settlement process 18. Critical to the operations of the TReDS is the mechanism that ensures timely settlement of funds between the member financiers and the MSME sellers (when the factoring unit is financed) and the subsequent settlement of funds between the member buyers and the respective financiers on due date of the factoring unit. In order to ensure a smooth process of such payments, the TReDS would be required to: a) Trigger settlement between financier and MSME for accepted bids - In respect of all factoring units financed on a given day, the TReDS will generate the payment obligations of all financiers on T+2 basis and send the file for settlement in any of the existing payment system as agreed among the system participants. The TReDS would have to put in place a separate recourse mechanism to handle settlement failures in respective payment systems. b) Trigger settlement between the buyer and the ultimate financier on due date - the TReDS would generate the payment obligations file and send the same for settlement on due date to the relevant payment system. 19. The TReDS will generate the settlement files and send the same to existing payment systems for actual payment of funds. This would ensure that the inter-bank settlement (between the bankers representing member MSMEs, buyers and the financiers) will take place and defaults, if any, by the buyers will be handled by the buyer’s bank and will not be the responsibility of the TReDS. Hence, the settlement process ensures payments to relevant recipients on due date, thus, facilitating the smooth operations on the TReDS. However, it would not entail a guaranteed settlement by the TReDS. 20. The TReDS would be required to put in place a mechanism for bankers to report defaults in payments by buyers. The TReDS would also need to ensure adequate arbitration and grievances redressal mechanism is in place. Regulatory framework for TReDS 21. The TReDS, which undertakes clearing and settlement activities, would be governed by the regulatory framework put in place by the Reserve Bank of India under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act 2007 (PSS Act). It will function as an authorised payment system under the PSS Act 2007. The activities of the TReDS as well as those of the participants in the TReDS would be governed by the relevant legal and regulatory provisions applicable to various stakeholders in the system. As such, the processes and procedures of the TReDS should be compliant with such legal and regulatory provisions which may be issued and amended from time to time by respective authorities. Eligibility criteria to set up and operate the TReDS 22. Entities desirous of setting up and operating the TReDS should fulfil the following criteria. (a) Financial Criteria (i) Since the TReDS will not be allowed to assume any credit risk, its minimum paid up equity capital shall be Rs. 25 crore. (ii) The foreign shareholding in the TReDS would be as per the extant foreign investment policy. (iii) Entities, other than the promoters, will not be permitted to have shareholding in excess of 10 per cent of the equity capital of the TReDS. (iv) The overall financial strength of the promoters/entity seeking to set up TReDS would be an important criteria of assessment/selection. (b) Due diligence of promoters The entities and their promoters/promoter groups as defined in the SEBI (Issue of Capital & Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2009 should be ‘fit and proper’ in order to be eligible to operate as TReDS. RBI would assess the ‘fit and proper’ status of the applicants on the basis of their past record of sound credentials and integrity; financial soundness and track record of at least 5 years in running their businesses. RBI may, inter alia, seek feedback on the applicants on these or any other relevant aspects from other regulators, and enforcement and investigative agencies like Income Tax, CBI, Enforcement Directorate, SEBI, etc. as deemed appropriate. (c) Technological capability The TReDS should have sound technological basis to support its operations. As such, the TReDS should, at the minimum, fulfil the following technological requirements.
Application procedure for Authorisation 23. The general guidelines as well as the application format for any non-bank entity to seek authorisation under the PSS Act for operating a payment system are available at /documents/87730/21647585/86707.pdf 24. Entities meeting the eligibility criteria as outlined in the Guidelines and desirous of setting up the TReDS, may apply in the prescribed format to the Chief General Manager, Department of Payment and Settlement Systems, Reserve Bank of India, 14th Floor, Central Office Building, Shaheed Bhagat Singh Marg, Mumbai – 400001, as and when the window for receipt of applications for this purpose is opened. Illustrative Outline of Process flow under TReDS a) Corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and Public Sector Undertakings, send purchase order to MSME seller (outside the purview of the TReDS). b) MSME seller delivers the goods along with an invoice. There may or may not be an accepted bill of exchange depending on the trade practice between the buyer and the seller (outside the purview of the TReDS). c) Thereafter, on the basis of either an invoice or a bill of exchange, the MSME seller creates a ‘factoring unit’ (which would be a standard nomenclature used in the TReDS for an invoice or a bill on the system) on TReDS. Subsequently, the buyer also logs on to TReDS and flags this factoring unit as ‘accepted’. In case of reverse factoring, this process of creation of factoring unit could be initiated by the buyer. d) Supporting documents evidencing movement of goods etc. may also be hosted by the MSME seller on the TReDS in accordance with the standard list or check-list of acceptable documents indicated in the TReDS. e) The TReDS will standardise the time window available for buyers to ‘accept’ the factoring units, which may vary based on the underlying document – an invoice or bill of exchange. f) The TReDS may have either a single or two separate modules for transactions with invoices and transactions with Bills of Exchange, if so required. In either case, all transactions routed through TReDS will, in effect, deal with factoring units irrespective of whether they represent an invoice or a bill of exchange. g) Factoring units may be created in each module as required. Each such unit will have the same sanctity and enforceability as allowed for physical instruments under the “Factoring Regulation Act, 2011” or under the “Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881” h) The standard format / features of the ‘factoring unit’ will be decided by the TReDS – it could be the entire bill/invoice amount or an amount after adjustment of tax / interest etc. as per existing market practice and as adopted as part of the TReDS procedure. However, each factoring unit will represent a confirmed obligation of the corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and PSUs, and will carry the following relevant details – details of the seller and the buyer, issue date (could be the date of acceptance), due date, tenor (due date – issue date), balance tenor (due date – current date), amount due, unique identification number generated by the TReDS, account details of seller for financier’s reference (for credit at the time of financing), account details of buyer for financier’s reference (for debit on the due date), the underlying commodity (or service if enabled). i) The TReDS should be able to facilitate filtering of factoring units (by financiers or respective sellers / buyers) on any of the above parameters. In view of the expected high volumes to be processed under TReDS, this would provide the necessary flexibility of operations to the stakeholders. j) The buyer’s bank and account details form an integral feature of the factoring unit. The creation of a factoring unit on TReDS shall result in automatic generation of a notice / advice to the buyer’s bank informing them of such units. k) These factoring units will be available for financing by any of the financiers registered on the system. The all-in-cost quoted by the financier will be available on the TReDS. This price can only be viewed by the MSME seller and not available for other financiers. l) There will be a window period provided for financiers to quote their bids against factoring units. Financiers will be free to determine the time-validity of their bid price. Once accepted by the MSME seller, there will be no option for financiers to revise their bids quoted online. m) The MSME seller is free to accept any of the bids and the financier will receive the necessary intimation. Financiers will finance the balance tenor on the factoring unit. n) Once a bid is accepted, the factoring unit will get tagged as “financed” and the funds will be credited to the seller’s account by the financier on T+2 basis (T being the date of bid acceptance). The actual settlement of such funds will be as outlined under the Settlement section. o) Once an accepted factoring unit has been financed by a financier, notice would be sent to buyer’s bank as well as seller’s bank. While the buyer’s bank would use this information to ensure availability of funds and also handle the direct debit to the buyer’s account on the due date in favour of the financier (based on the settlement obligations generated by the TReDS), the seller’s bank will use this input to adjust against the working capital of the MSME seller, as necessary (the TReDS procedures may, if necessary, also indicate that the proceeds of the accepted and financed factoring units will be remitted to the existing working capital / cash credit account of the MSME seller). If agreed by members, the TReDS may also provide the option to members, whereby the financiers would take direct exposure against the buyers rather than through their bankers. p) On the due date, the financier will have to receive funds from the buyer. The TReDS will send due notifications to the buyers and their banks advising them of payments due. The actual settlement of such funds will be as outlined under the Settlement section. q) Non-payment by the buyer on the due date to their banker should tantamount to a default by the buyer (and be reported as such as per regulatory procedures prescribed from time to time) and enable the banker to proceed against the buyer. Any action initiated in this regard, will be strictly non-recourse with respect to the MSME sellers and outside the purview of the TReDS. r) These instruments may be rated by the TReDS on the basis of external rating of the buyer, its credit history, the nature of the underlying instrument (invoice or bill of exchange), previous instances of delays or defaults by the buyer with respect to transactions on TReDS, etc. s) The rated instruments may then be further transacted / discounted amongst the financiers in the secondary segment. t) Similar to the primary segment, any successful trade in the secondary segment will also automatically result in a direct debit authority being enabled by the buyer’s bank in favour of the financier (based on the settlement obligations generated by the TReDS). In parallel, it will also generate a ‘notice of assignment’ intimating the buyer to make the payment to the new financier. u) In the event that a factoring unit remains unfinanced, the buyer will pay the MSME seller outside of the TReDS. In order to meet the requirements of various stakeholders, the TReDS should ensure to provide various types of MIS reports including intimation of total receivables position, financed and unfinanced (to sellers); intimation of outstanding position, financed and unfinanced with details of beneficiaries and beneficiary accounts to be credited (for buyers); total financed position for financiers; etc. Similarly, data on unfinanced factoring units in the market should also be made available by the TReDS. The system should also generate due date reminders to relevant parties, notifications to be issued to bankers when a factoring unit is financed, notifications to be issued to buyers once a factoring unit related to their transaction is traded in the secondary segment, etc. |
Procedural Guidelines
| National Electronic Funds Transfer System - Procedural Guidelines | |
|---|---|
|
Sl. |
Subject |
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
Definitions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
5 |
Procedure for Participation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Process Flow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
d) Transmission / Submission of NEFT Message to the NEFT Clearing Centre |
|
|
e) Processing and Transmission of NEFT Message to the Beneficiary Banks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i) Acknowledgement / Positive Confirmation by the Beneficiary Bank and Return in Case of Non-Credit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Inter-Bank Settlement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
Rights and Obligations |
|
|
a) General Rights and Obligations of the Sender / Originator, Participating Banks or Institutions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
Annexures |
|
|
I |
|
|
II |
|
|
III |
|
|
IV |
|
|
NATIONAL ELECTRONIC FUNDS TRANSFER (NEFT) SYSTEM Reserve Bank of India has introduced an electronic funds transfer system called "National Electronic Funds Transfer” System (hereinafter referred to as "NEFT System" or "NEFT" or “System”, as appropriate). A set of procedures to be followed by various stakeholders to the system are detailed in this document. The objective of the NEFT System is to establish an electronic funds transfer system to facilitate an efficient, secure, economical, reliable and expeditious system of funds transfer and clearing in the banking sector throughout India, and to relieve the stress on the existing paper based funds transfer and clearing system. In these Procedural Guidelines, unless the context otherwise requires : (a) "Acceptance" means execution of payment instruction. (b) "Bank" means a banking company as defined in Section 5 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, and includes the State Bank of India, constituted by the State Bank of India Act, 1955, a subsidiary bank constituted under the State Bank of India (Subsidiary Banks) Act, 1959, a corresponding new bank under Section 3 of the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1970 and a corresponding new bank constituted under the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1980, a co-operative bank, as defined in Section 56 of Part V of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (AACS) and such other banks as may be specified from time to time. (c) "Beneficiary" means the person designated as such, and to whose account payment is directed to be made in a payment instruction. (d) "Beneficiary / Destination Bank / Branch" means the branch of the bank / branch identified in a payment instruction which is maintaining the account of the beneficiary. (e) "NEFT Clearing Centre" means any office designated by the Nodal Department for receiving, processing and sending the NEFT SFMS message and the debiting and crediting of accounts of the participating banks and institutions for settlement of payment obligations or one or more of these functions. The National Clearing Cell, Reserve Bank of India, Nariman Point, Mumbai has been designated as the NEFT Clearing Centre (NCC) for purposes of the NEFT System. (f) "NEFT SFMS message" means an electronic Structured Financial Messaging Solution (SFMS) message containing a batch of NEFT payment instructions for funds transfer, processed and consolidated in the manner specified for transmission of payment instructions from NEFT Service Centre to the NEFT Clearing Centre. (g) "NEFT Service Centre" means an office or branch of a bank in a centre designated by that bank to be responsible for processing, sending or receiving NEFT SFMS message on behalf of that bank in that Centre and to do all other functions entrusted to a NEFT Service Centre by or under these guidelines. NEFT Service Centre is referred to as "Sending NEFT Service Centre" when it originates an NEFT SFMS message for funds transfer. NEFT Service Centre is referred to as "Receiving NEFT Service Centre" when it receives a NEFT SFMS message from the NEFT Clearing Centre. (h) "NEFT System" means the National Electronic Funds Transfer System established by these guidelines for carrying out inter-bank funds transfers within India (and from India to Nepal), and providing for settlement of payment obligations arising out of such funds transfers, among the participating banks. (i) "Execution" of a payment instruction in relation to a sending bank means the transmission or sending of the payment instruction by it to the NEFT Service Centre; in relation to a Service Centre it means transmission of the consolidated payment instruction in the encrypted NEFT SFMS message to the NEFT Clearing Centre. (j) "Funds Transfer" means the series of transactions beginning with the issue of originator's payment instruction to the sending bank and completed by acceptance of payment instruction by the beneficiary's bank for the purpose of making payment to the beneficiary of the instruction. (k) "Nodal Department" means the Department of Payment and Settlement Systems of Reserve Bank of India, NEFT Clearing Centre and the Mumbai Regional Office of the Reserve Bank of India which are responsible for implementation, administration and supervision of the NEFT System. (l) "Notified" means communicated electronically or in writing. (m) "Originator / Sender" means the person who issues a payment instruction to the sending bank. (n) "Participating Bank” means a bank admitted for participating in the NEFT System pursuant to Paragraph 3.1 of these Guidelines and whose Letter of Admission has not been cancelled. (o) "Payment Instruction" means an unconditional instruction issued by an originator in writing or transmitted electronically to a sending bank to effect a funds transfer for a certain sum of money expressed in Indian Rupees, to the designated account of a designated beneficiary by debiting correspondingly an account of the originator or through remittance of cash. (p) "Public Sector Bank" means State Bank of India, constituted by the State Bank of India Act, 1955, subsidiary banks constituted under the State Bank of India (Subsidiary Banks) Act, 1959, the banks constituted under Section 3 of the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1970 and the banks constituted under Section 3 of the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of Undertakings) Act, 1980. IDBI Bank has since been classified as a Public Sector Bank. (q) "Reserve Bank of India" means the Reserve Bank of India or RBI established under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (2 of 1934). (r) "Security Procedure" means the set of procedural guidelines at Paragraphs under the Sections of these Guidelines for the purpose of :
(s) "Sending / Originating Bank" means the branch of a bank, which receives payment instruction from its customer or any other person for transfer of funds to the account with another bank participating in NEFT. When the originator is a participating institution, reference to sending bank shall be construed as referring to the NEFT Service Centre. (t) "Settlement Account" means an account maintained by a participating bank or institution for the purpose of settlement of payment obligations under the NEFT System. (u) "Valid Reasons of Non-payment" are the reasons due to which the beneficiary bank fails to or cannot make payment to the beneficiary. Some illustrative reasons are :
(v) "SFMS Message" means an electronic Structured Financial Messaging Solution (SFMS) message containing a batch of payment instructions for funds transfer, processed and consolidated in the manner specified for transmission of payment instructions and communication related thereto. (w) "Credit" means credit received by the NEFT member through the NEFT System, which has to be ultimately credited to the account of the beneficiary customer at the concerned branch of the beneficiary bank, after due verification thereof. (x) "IFSC" means Indian Financial System Code used to identify a participating bank branch in the NEFT SFMS message. These procedural guidelines shall apply to all NEFT-enabled participating banks / and branches in the system as notified by Reserve Bank of India from time to time on its official website at the link http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/neft.aspx. 5. Procedure for Participation (i) Admission : To be eligible to apply for admission as a participating bank, an applicant –
Provided that, all or any of the above conditions may be relaxed or dispensed with, if so decided by the Reserve Bank of India. List of participant banks and bank-branches will be displayed on website of Reserve Bank of India under the link http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/neft.aspx. Any bank or institution desirous of participating in the NEFT System as a participating bank may submit to the Regional Director, Reserve Bank of India, Mumbai Regional Office, Shahid Bhagat Singh Marg, Fort, Mumbai – 400 001, duly authenticated application, containing full particulars in the form specified at Annexure I (Form : NEFT-IA). Every application shall be accompanied by an undertaking in the specified form to abide by the Procedural Guidelines in the event of admission. Letter of Admission as specified in Annexure II (Form : NEFT-IB) to every bank admitted to the NEFT System will be issued by Reserve Bank of India.
(iii) Withdrawal from Participation :
(iv) Cancellation of Letter of Admission : Letter of admission issued to a bank may be cancelled by the Reserve Bank on it being satisfied that such bank has –
No order of cancellation shall be passed without first giving an opportunity of hearing to the bank concerned. Every order of cancellation shall be notified to the respective bank and also to all other participating banks in the NEFT System. Notwithstanding the order of cancellation of Letter of Admission passed against it, such bank shall discharge all its payment obligations arising out of the funds transfers effected in the NEFT System. The parties to a funds transfer under this NEFT System are the sending bank, the sending Service Centre, the NEFT Clearing Centre, the receiving Service Centre and the beneficiary branch. (i) Request for NEFT by a Bank Customer / Any Person
(ii) Data Entry at the Sending Bank Branch The sending bank branch shall prepare the SFMS message as and when the applications for funds transfer is received and arrange to send the message to NEFT Service Centre till the cut off time for the batch. (iii) Processing / Data Upload at Sending NEFT Service Centre The sending NEFT Service Centre shall accept the messages received from branches / customers through net banking platform if these are complete / in order and received within cut-off time or reject the same if the messages are incomplete / not confirming to the parameters specified. (iv) Transmission / Submission of NEFT Message to the NEFT Clearing Centre The sending Service Centre shall transmit the NEFT SFMS message to the NEFT Clearing Centre by using the communication network designated by Reserve Bank of India. (v) Processing and Transmission of NEFT Message to the Beneficiary Banks After consolidating all NEFT messages received from originating banks, the NEFT Clearing Centre shall process the data, arrive at fund settlement, send the fund file to Deposit Accounts Department (DAD), RBI for settlement and after settlement is over, send beneficiaries' details / data to each beneficiary bank for affording credit to the beneficiaries' accounts. Banks which have no transactions will get a batch wise 'nil' transactions report and a summary report at the end of the day indicating all inward transactions received by them during the day. NEFT messages generated for destination banks will be transmitted to the NEFT Service Centre of each beneficiary bank using SFMS. (vi) Data Validation at the Receiving NEFT Service Centre On receipt of the NEFT message, the receiving NEFT Service Centre shall process these files and forward them to the beneficiary branches using SFMS. Alternatively, the receiving NEFT Service Centre may use the Straight Through Processing (STP) interface available in SFMS and upload these NEFT messages to their internal banking solution directly, to afford the credits to the beneficiary accounts centrally. The beneficiary branches would make payment to the beneficiaries within two hours of batch settlement time by crediting the specified account of the beneficiary or otherwise placing funds at the disposal of the beneficiary. (viii) Revocation of Payment Instruction A payment instruction issued for execution shall become irrevocable when it is executed by the sending bank. Any revocation, after the payment instruction is executed by the sending bank shall not be binding on any other party in the NEFT system. (ix) Acknowledgement / Positive Confirmation by the Beneficiary Bank and Return in Case of Non-Credit NEFT presently functions with a Batch+2 (B+2) return cycle. The B+2 return discipline would require banks to afford credit to the beneficiaries' account immediately upon completion of a batch else return the transactions within two hours of completion of the batch settlement, if it is not possible to afford credits to the beneficiaries, for any reason. Therefore, an inward credit message which is not returned within two hours from the time at which the payment instructions are processed at NEFT Centre (B+2) is treated to have been completed and credit afforded to the beneficiary's account by the beneficiary branch. It is, therefore, vital that uneffected credits are re-transmitted back as return NEFT transactions in the immediate next batch itself. In addition to this, in order to facilitate the originator of NEFT to receive a confirmation of credit being afforded to Beneficiary's account, the originator may indicate his / her mobile number or email-id in his / her NEFT application while initiating the transaction. After successfully crediting the Beneficiary's account, the beneficiary bank will send a Credit Acknowledgement message indicating “credited to customers' account” to the originating bank through NEFT Service Centre. The originating banks after receiving the positive confirmation message from the beneficiary bank, shall initiate a mobile SMS or generate an e-mail to the originator to convey the fate of the transaction. (x) Sender to be Advised in Case of Returns If the beneficiary specified in the sender's payment instruction fails to get payment through the NEFT system for some valid reasons, the sender shall be informed immediately after the sending bank gets the returned NEFT. The sending bank shall also arrange to make payment to the sender by crediting the account of the sender or otherwise placing funds at the disposal of the sender. The originating bank shall provide the description “NEFT-Return” in the pass book / account statement of the originator whose NEFT transaction is returned. In case of returns pertaining to the outward transactions initiated by a non-customer, the initiator to be advised immediately by referring to the contact details provided, earlier, and funds to be kept at his / her disposal. (xi) Beneficiary to be Advised of the Receipt of Funds After crediting the account of the beneficiary, the beneficiary bank shall advise the beneficiary of the funds received. The Account Statement / Pass Book entry or any online messaging system shall indicate briefly the source of funds as well. For this purpose, the mandatory field 6091 which contains the remitter's name shall be picked up for the source of credit and information contained shall be printed in the Account Statement / Pass Book. Banks originating transactions shall ensure proper and meaningful details are provided in this field. Description of field 6091 is M 6091 Sending customer a/c name 50x Sender's account name NEFT will function on all the RTGS working days and the banks participating in NEFT are required to participate on all such working days. The list of holidays for RTGS / NEFT is available in the website of RBI at http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/HolidayMatrixDisplay.aspx. (i) Inter-bank Funds Settlement at Reserve Bank : Every participating bank and admitted institution shall open and maintain in the NEFT Clearing Centre, Mumbai, a settlement account for settlement of payment obligations arising under the funds transfer executed under the NEFT system. (ii) Finality of Settlement : The settlement so arrived by through multilateral netting shall be final and irrevocable, in terms of section 23 of the “Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007” as soon as the same is determined in terms of the procedures notified by RBI. (iii) Settlement and Default Handling Procedure : Aspects relating to finality of settlement and default handling in the event of failure-to-settle situations will be in accordance with the Directive on Settlement and Default Handling Procedures issued by RBI and as duly amended from time to time. The continued eligibility of a bank to participate shall be reviewed in case of permanent default by a member bank. Default will be considered permanent if the process of recalculation provided as part of the default handling procedure is necessitated in respect of a participant bank on more than three occasions in a calendar month. The number of occasions shall be calculated separately for each multilateral and deferred net settlement system. (i) General Rights and Obligations of Sender / Originator, Participating Banks or Institutions Every participating bank or institution shall maintain the security, integrity and efficiency of the System. (ii) Rights and Obligations of the Sender / Originator (a) Funds transfer instruction shall be issued by the sender / originator in a manner prescribed by the participant bank. (b) The format shall be complete and contain all requisite particulars. The sender or the originator shall be responsible for the accuracy of the particulars given in the payment instructions and special care should be taken for account number of the beneficiary, etc. (c) The sender / originator shall be bound by any payment instruction executed by the bank if the bank had executed the payment instruction in good faith and in compliance with the security procedure, provided that the sender / originator shall not be bound by any payment instruction executed by the bank, if he proves that the same was not issued by him and that it was caused either by negligence or a fraudulent act of any employee of the bank. (d) The sender / originator shall ensure availability of funds in his / her account or remit cash while issuing the payment instruction to his / her bank. (e) The payment instruction shall become irrevocable once it is executed by the bank. The bank is not bound by any notice of revocation unless it is not in compliance with the security procedure. (f) In the event of any delay or loss on account of error, negligence or fraud on the part of an employee of the beneficiary bank in the completion of funds transfer pursuant to receipt of payment instruction by the beneficiary bank leading to delayed payment to the beneficiary, the beneficiary bank shall pay compensation (at current RBI LAF Repo Rate plus two percent) for the period of delay. In the event of delay in return of funds transfer instruction for any reason whatsoever, the beneficiary bank shall refund the amount together with interest (at current RBI LAF Repo Rate plus two percent) till the date of refund. (g) During the NEFT operating hours, originating banks shall endeavour to put through the request for NEFT transactions received by them, either online or across the counters, preferably in the next available batch, but, in any case, not exceeding two hours from the time of receipt of requests. In the likelihood of any delay / possible delay in adhering to this requirement, the sender / originator shall be informed of the delay / possible delay and the reasons for the same. (h) Customers can complain to the Banking Ombudsman if the complaint is not resolved to his / her satisfaction within thirty days. (iii) Rights and Obligations of Sending Bank
(iv) Obligations of the Sending NEFT Service Centre
(v) Obligations of NEFT Clearing Centre The NEFT Clearing Centre shall comply with the time schedule, process and sort the SFMS messages bank-wise and after debiting / crediting the settlement accounts with the corresponding value, transmit the NEFT SFMS messages to the respective receiving NEFT Service Centres. The NEFT Clearing Centre shall generate, dispatch and maintain records of transactions. The Clearing Centre shall maintain record of all payment instructions processed by it for a period of ten years in terms of guidelines issued by RBI under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act on preservation of information / data / record pertaining to payment system applications. (vi) Obligations of the Receiving NEFT Service Centre
(vii) Rights and Obligation of Beneficiary Bank
The service charges to be levied by the originating banks would be in terms of the instructions issued from time to time under the framework of charges to be levied by the banks for offering various electronic products There are no processing charges levied by the NEFT Clearing Centre up to March 31, 2011. The same would be reviewed periodically. The RBI may, if it so desires in future, decide to levy any other charge / fee as also the quantum thereof. Beneficiary Banks would not claim service charge for passing on the credit to the beneficiaries. 10. Dispute Resolution Mechanism The mechanism for resolution of disputes will be in accordance with the Directive on Dispute Resolution Mechanism issued by RBI and as duly amended from time to time. 11. Amendment to Procedural Guidelines The Procedural Guidelines can be amended only by RBI. RBI may also, by issuance of a circular, amend the procedure. Form NEFT-1A Ref. No.... . . . . . .. .. .. . Date The Regional Director Madam / Dear Sir, Application for participation in NEFT System Our bank requests Reserve Bank of India's approval for participation in the NEFT System and agrees to abide by the Procedural Guidelines for the NEFT System. Our bank satisfies the eligibility criteria devised in paragraph 5 (i) and Annexure IV of the NEFT Procedural Guidelines and documentary evidence in support of that are attached herewith for your perusal. In the event of being admitted to the System, we would comply with the technical and operational requirements of the NEFT System and would meet the settlement obligations from our account/s maintained with Reserve Bank of India. (.........................................................................) Place : Enclosures : As stated above No. of Core Banking-enabled branches that can participate in NEFT : Form NEFT-1B Reserve Bank of India NEFT System – Letter of Admission Reference No. Date : To ................................... Madam / Dear Sir, Please refer to your application no…………………..dated .........................for participation in the NEFT System. It is advised that your bank has been admitted for participation in the NEFT system with effect from . . . . . . . You are required to comply with the technical and operational requirements as indicated in the Procedural Guidelines for NEFT System and confirm your readiness latest by ……….. . . (.........................................................................) |
|
 |
|
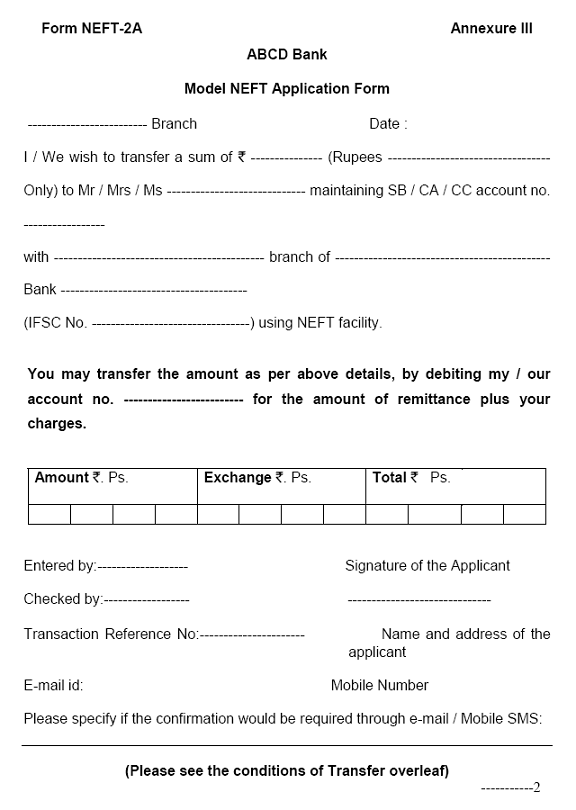
Form NEFT-2A Conditions for transfer of funds through NEFT 1. I / We have checked the funds transfer instructions / particulars given in the application and I / We shall be liable to compensate the Bank for any loss arising on account of any error in payment order / amendment / cancellation thereto. 2. I / We understand that the messages given after cut-off time will be sent only on the next batch / working day. 3. The transfer is effected for legitimate personal / business needs. 4. I / We shall ensure availability of funds properly applicable to the payment order before execution of the payment order by the bank and understand that if the bank executes the transfer order without properly applicable funds being available in my account, I / We shall be bound to pay to the bank the amount debited to my account together with charges including interest payable to the bank provided the transfer was effected as per my order. 5. I / We understand that in case the payee branch does not have NEFT facility, the funds will be credited back to my / our account as and when it is returned by the beneficiary bank. 6. I / We agree that in the event of any delay in the completion of the funds transfer or any loss on account of error in the execution of the funds transfer pursuant to my / our payment order, the bank's liability shall be limited to the extent of the amount involved in the funds transfer plus interest (at the RBI LAF Repo rate plus two percent) for any period of delay. 7. I / We also agree to abide with all the other terms and conditions contained in the model agreements / application forms or other terms / rules / regulations governing NEFT transactions as enumerated by RBI. (Signature of the Applicant) Date : |
|
Eligibility Criteria for Participation in NEFT System |
||
|
Sl. No. |
Category of banks |
Access to NEFT |
|
1. |
Scheduled Commercial Banks (excluding Regional Rural Banks and Local Area Banks) |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • CRAR 9% • Net NPAs less than 10% • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year • Net profit in at least one of the preceding two years; and • Minimum net - worth of ` 50 crore |
|
2. |
State Co-operative Banks |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year; and • Minimum net -worth of `. 50 crore |
|
3. |
District Central Co-operative Banks |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year; and • Minimum net - worth of ` . 50 crore |
|
4. |
Regional Rural Banks |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year; and • Minimum net - worth of ` . 50 crore |
|
5. |
Local Area Banks |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • CRAR 9% • Net NPAs less than 10% • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year • Net profit in at least one of the preceding two years; and • Minimum net - worth of ` . 50 crore |
|
6. |
Scheduled Urban Co-operative Banks |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • CRAR 9% • Net NPAs less than 10% • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year • Net profit in at least one of the preceding two years; and • Minimum net - worth of ` . 50 crore |
|
7. |
Non-Scheduled Urban Cooperative Banks |
Type A Membership of RTGS subject to • CRAR 9% • Net NPAs less than 10% • No default in maintenance of CRR and SLR during the past one year • Net profit in at least one of the preceding two years; and • Minimum net - worth of ` . 50 crore |
|
8. |
Banks in category 1, and 3-7 not complying with the requirements |
No access |
|
9. |
Unlicensed banks (other than unlicensed State Co-operative Banks and District Central Co-operative Banks) |
No access |
List of Banks Permitted to Provide Mobile Banking Service in India
| List of Banks permitted to provide Mobile Banking Service in India – Position as on August 29, 2023 | |
|---|---|
| Sl. No. | Name of the bank |
| 1. | 510 Army Base Workshop Credit Co-operative Primary Bank Ltd. |
| 2. | Abhyudaya Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 3. | Abhinandan Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 4. | ACE Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 5. | Adarniya P. D. Patilsaheb Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 6. | Adarsh Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 7. | Adarsh Mahila Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 8. | Ahmednagar Merchants Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 9. | Ahmednagar Shahar Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 10. | Airtel Payments Bank Limited |
| 11. | Ajantha Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 12. | Akhand Aanand Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 13. | Alavi Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 14. | Allahabad UP Gramin Bank |
| 15. | Aman Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 16. | Amarnath Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 17. | Ambajogai Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 18. | Ambarnath Jai-Hind Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 19. | American Express Banking Corporation |
| 20. | Amreli Jilla Madhyastha Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 21. | Amreli Nagarik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 22. | Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank |
| 23. | Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank |
| 24. | A P Mahesh Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 25. | Apna Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 26. | Appasaheb Birnale Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 27. | Arihant Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 28. | Arunachal Pradesh Rural Bank |
| 29. | Arvind Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 30. | Aryavart Bank |
| 31. | Assam Gramin Vikash Bank |
| 32. | Associate Co-operative Bank Limited, Surat |
| 33. | Astha Mahila Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 34. | Au Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 35. | Axis Bank Limited |
| 36. | Balasinor Nagarik Sahkari Bank Limited |
| 37. | Balitikuri Cooperative Bank Ltd. |
| 38. | Balotra Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 39. | Balusseri Co-op. Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 40. | Bandhan Bank Limited |
| 41. | Bank of America NA |
| 42. | Bank of Bahrain & Kuwait B.S.C. |
| 43. | Bank of Barodaµ |
| 44. | Bank of India |
| 45. | Bank of Maharashtra |
| 46. | Bangiya Gramin Vikash Bank |
| 47. | Baran Nagrik Sahkari Bank Limited, Baran |
| 48. | Barclays Bank PLC |
| 49. | Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bankƛ |
| 50. | Baroda Rajasthan Kshetriya Gramin Bank |
| 51. | Baroda Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank |
| 52. | Bassein Catholic Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 53. | Bellad-Bagewadi Urban Souharda Sahakari Bank Nyt. |
| 54. | Betul Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 55. | Bhadradri Co-operative Urban Bank |
| 56. | Bhagini Nivedita Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 57. | Bhausaheb Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 58. | Bhausaheb Birajdar Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 59. | Bhavani Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 60. | Bhilwara Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 61. | BNP Paribas |
| 62. | Bombay Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 63. | Brahmadeodada Mane Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 64. | Capital Local Area Bank Limited |
| 65. | Canara BankΩ |
| 66. | Catholic Syrian Bank Limited |
| 67. | Central Bank of India |
| 68. | Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank |
| 69. | Chaitanya Mahila Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 70. | Chartered Sahakari Bank Niyamitha |
| 71. | Cherpalcheri Co-op. Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 72. | Chhattisgarh Rajya Gramin Bank |
| 73. | Chhattisgarh Rajya Sahakari Bank Marayadit |
| 74. | Chiplun Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 75. | Chittorgarh Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 76. | Citi Bank N.A. |
| 77. | Citizens Co-operative Bank Limited, Noida |
| 78. | Citizen Credit Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 79. | City Union Bank Limited |
| 80. | Coastal Local Area Bank Limited |
| 81. | Colour Merchants’ Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 82. | Col RD Nikam Sainik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 83. | Contai Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 84. | Daivadnya Sahakara Bank Niyamit |
| 85. | Dakshin Bihar Gramin Bank€ |
| 86. | Dapoli Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 87. | Dattatray Maharaj Kalambe Jaoli Sahakari Bank |
| 88. | Dausa Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd |
| 89. | Davangere District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 90. | DBS Bank India Limited |
| 91. | DCB Bank Limited |
| 92. | Deendayal Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 93. | Deogiri Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd., Aurangabad |
| 94. | Deutsche Bank AG |
| 95. | Development Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 96. | Dhanera Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 97. | Dhule Vikas Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 98. | Doha Bank QSC |
| 99. | Dr.Annasaheb Chougule Urban Co-op. Bank Limited |
| 100. | Dr. Appasaheb Urf Sa. Re. Patil Jaysingpur-Udgaon Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 101. | D. T. Patil Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 102. | Durgapur Steel Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 103. | Eluru Co-operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 104. | Equitas Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 105. | ESAF Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 106. | Excellent Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 107. | Fincare Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 108. | Fingrowth Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 109. | Fino Payments Bank Limited |
| 110. | Gautam Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 111. | Gayatri Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 112. | Godavari Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., Nashik |
| 113. | Gondal Nagrik Sahkari Bank Ltd. |
| 114. | GP Parsik Sahakari Bank Ltd., Kalwa, Thane |
| 115. | Guardian Souharda Sahakari Bank Niyamita |
| 116. | Gujarat Ambuja Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 117. | Hadagali Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 118. | Haveli Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 119. | HDFC Bank Limited |
| 120. | Himachal Pradesh Gramin Bank |
| 121. | Himatnagar Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 122. | Hooghly District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 123. | Hutatma Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 124. | ICICI Bank Limited |
| 125. | IDBI Bank Limited |
| 126. | IDFC FIRST Bank Limited |
| 127. | Idukki District Co-operative Bank |
| 128. | India Post Payments Bank Limited |
| 129. | Indian Bankℼ |
| 130. | Indian Overseas Bank |
| 131. | Indore Cloth Market Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 132. | Indore Paraspar Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 133. | Indore Premier Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 134. | Indraprastha Sehkari Bank Limited |
| 135. | Indrayani Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 136. | IndusInd Bank Limited |
| 137. | Irinjalakuda Town Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 138. | J & K Grameen Bank |
| 139. | Jalgaon Janata Sahakari Bank |
| 140. | Jalna Merchants Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 141. | Jalore Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 142. | Jamia Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 143. | Jammu & Kashmir Bank Limited |
| 144. | Jampeta Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 145. | Jana Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 146. | Janakalyan Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 147. | Jankalyan Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 148. | Janaseva Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 149. | Janata Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 150. | Janata Sahakari Bank Limited, Ajara |
| 151. | Janata Sahakari Bank Limited, Pune |
| 152. | Janatha Seva Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 153. | Jayprakash Narayan Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 154. | Jharkhand Rajya Gramin Bank |
| 155. | Jijamata Mahila Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 156. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Maryadit, Ambikapur |
| 157. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Mydt., Durg |
| 158. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Maryadit, Jagdalpur |
| 159. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Maryadit, Khargone |
| 160. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Maryadit, Raipur |
| 161. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Maryadit, Rajnandgaon |
| 162. | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Mydt., Vidisha |
| 163. | Jio Payments Bank Limited |
| 164. | Jivan Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 165. | Jodhpur Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 166. | Jogindra Central Cooperative Bank Ltd. |
| 167. | JP Morgan Chase Bank NA |
| 168. | Jugalkishore Tapdiya Shree Mahesh Urban Co-operative Bank |
| 169. | Kallappanna Awade Ichalkaranji Janata Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 170. | Kangra Co-operative Bank |
| 171. | Kankaria Maninagar Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 172. | Kannur District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 173. | Karnataka Bank Limited |
| 174. | Karnataka Gramin Bank* |
| 175. | Karnataka Mahila Sahakara Bank Niyamitha |
| 176. | Karnataka Vikas Grameena Bank |
| 177. | Karur Vysya Bank Limited |
| 178. | Kashi Gomti Samyut Gramin Bank |
| 179. | Kashmir Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 180. | Kerala Gramin Bank@ |
| 181. | Khattri Co-operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 182. | Khardah Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 183. | Koilkuntla Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 184. | Kolhapur District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 185. | Kolhapur Mahila Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 186. | Kota Nagrik Sahkari Bank Limited |
| 187. | Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited© |
| 188. | Kottayam Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 189. | Koyana Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 190. | Krishna Bhima Samruddhi Local Area Bank Limited |
| 191. | Krishna District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd. |
| 192. | Krishna Mercantile Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 193. | Lakhimpur Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 194. | Langpi Dehangi Rural Bank |
| 195. | Laxmi Mahila Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 196. | Laxmi Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 197. | L.I.C. Employees' Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 198. | Liluah Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 199. | Lokmangal Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 200. | Loknete Dattaji Patil Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 201. | Lokvikas Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 202. | Lonawala Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 203. | Mahalakshmi Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 204. | Mahanagar Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 205. | Maharashtra Gramin Bank |
| 206. | Maharashtra Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 207. | Mahatma Fule Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 208. | Mahaveer Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 209. | Mahesh Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 210. | Mahesh Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd., Ahmedpur |
| 211. | Makarpura Industrial Estate Co-op Bank Ltd. |
| 212. | Malda District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 213. | Malviya Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 214. | Manipur Rural Bank |
| 215. | Mann Deshi Mahila Sahkari Bank Limited |
| 216. | Mansing Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 217. | Manvi Pattana Souharda Sahakari Bank Niyamitha |
| 218. | Mahesh Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 219. | Mahila Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Mahasamund |
| 220. | Manwath Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 221. | Maratha Co-operative Bank Limited, Belgaum |
| 222. | Meghalaya Rural Bank |
| 223. | Mehsana District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 224. | Merchants' Co-operative Bank Ltd., Tiptur |
| 225. | Merchant's Liberal Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 226. | Mizoram Cooperative Apex Bank Ltd. |
| 227. | Mizoram Rural Bank |
| 228. | Model Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 229. | M. P. Rajya Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 230. | M.S. Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 231. | Mugberia Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 232. | Muzaffarnagar District Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 233. | Nadia District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 234. | Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Durg |
| 235. | Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Gwalior |
| 236. | Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Vidisha |
| 237. | Nandani Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 238. | Narmada Jhabua Gramin Bank£ |
| 239. | Nashik Zilha Sarkari and Parishad Karmachari Sahakari Bank Niyamit |
| 240. | Nasik Road Devlali Vyapari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 241. | Navanagara Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 242. | Navi Mumbai Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 243. | Navsarjan Industrial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 244. | New India Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 245. | Nidhi Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 246. | Nilambur Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 247. | NKGSB Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 248. | North East Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 249. | Northern Railway Multi State Primary Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 250. | NSDL Payments Bank Limited |
| 251. | Nutan Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 252. | Omprakash Deora People’s Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 253. | Pali Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 254. | Pallavan Grama Bank |
| 255. | Palus Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 256. | Pandyan Grama Bank |
| 257. | Paschim Banga Gramin Bank |
| 258. | Patan Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 259. | Pavana Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 260. | Paytm Payments Bank Limited |
| 261. | People's Co-operative Bank Limited, Dholka |
| 262. | Pochampally Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 263. | Poornawadi Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 264. | Porbandar Commercial Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 265. | Pragati Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 266. | Prathama Bank |
| 267. | Prathamik Shikshak Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 268. | Prerana Co-operative Bank Limited, Pune |
| 269. | Prime Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 270. | Priyadarshani Nagari Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 271. | Priyadarshani Urban Co-operative Bank |
| 272. | Progressive Mercantile Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 273. | Puduvai Bharthiar Grama Bank |
| 274. | Pune Cantonment Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 275. | Pune District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 276. | Pune People’s Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 277. | Pune Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 278. | Punjab Gramin Bank¥ |
| 279. | Punjab National Bankα |
| 280. | Punjab & Maharashtra Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 281. | Punjab & Sind Bank |
| 282. | Purvanchal Bank |
| 283. | Pusad Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 284. | Raigad District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 285. | Rajapur Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 286. | Rajarambapu Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 287. | Rajarshi Shahu Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 288. | Rajasthan Marudhara Gramin Bank |
| 289. | Rajadhani Co-op. Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 290. | Raje Vikramsinh Ghatge Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 291. | Rajgurunagar Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 292. | Rajkot Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 293. | Rajkot Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 294. | Rajlaxmi Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 295. | Rampur Zila Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 296. | Ramrajya Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 297. | Rani Channamma Mahila Sahakari Bank Niyamit, Belagavi |
| 298. | Ratnagiri District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 299. | RBL Bank Limited |
| 300. | Reserve Bank Employees’ Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 301. | Sadalga Urban Souharda Sahakari Bank Niyamit |
| 302. | Sadhana Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 303. | Sadhana Sahakari Bank Limited, Nagpur |
| 304. | Saibaba Nagari Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 305. | Sahakarmaharshi Bhausaheb Thorat Amrutvahini Sahakari Bank Ltd |
| 306. | Samarth Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 307. | Samarth Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Jalna |
| 308. | Samata Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 309. | Samata Co-operative Development Bank Ltd. |
| 310. | Sampada Sahakari Bank Limited, Pune |
| 311. | Samruddhi Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 312. | Sandur Pattana Souharda Sahakari Bank Niyamitha |
| 313. | Sanmitra Mahila Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 314. | Sant Sopankaka Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 315. | Saptagiri Grameena Bank |
| 316. | Sarakari Naukarara Sahakari Bank Niyamit |
| 317. | Saraspur Nagarik Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 318. | Sardargunj Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited, Anand |
| 319. | Sardargunj Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited, Patan |
| 320. | Sardar Singh Nagarik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 321. | Sardar Vallabhbhai Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 322. | Sarva Haryana Gramin Bank |
| 323. | Sarva U P Gramin Bank |
| 324. | Sarvodaya Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 325. | Saurashtra Gamin Bank |
| 326. | Sharad Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 327. | SBM Bank (India) Ltd. |
| 328. | Shinhan Bank |
| 329. | Shivajirao Bhosale Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 330. | Shivalik Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 331. | Shramik Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 332. | Shree Balaji Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 333. | Shree Basaveshwar Urban Co-op Bank Ltd. |
| 334. | Shree Dharati Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 335. | Shree Kadi Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 336. | Shree Mahalaxmi Urban Co-op. Credit Bank Ltd. , Gokak |
| 337. | Shree Mahavir Sahakari Bank Limited, Jalgaon |
| 338. | Shree Mahayogi Lakshmamma Co-op Bank Limited |
| 339. | Shree Mahesh Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 340. | Shree Mahuva Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 341. | Shree Panchganga Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 342. | Shree Sharada Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 343. | Shree Talaja Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 344. | Shree Vardhaman Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 345. | Shree Warana Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 346. | Shri Adinath Co-operative Bank Limited, Ichalkaranji |
| 347. | Shri Anand Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 348. | Shri Arihant Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 349. | Shri Basaveshwar Sahakari Bank Niyamith, Bagalkot |
| 350. | Shri Bharat Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 351. | Shri Chatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Sahakari Bank Niyamith |
| 352. | Shri Chhani Nagrik Sahkari Bank Ltd. |
| 353. | Shri Chhatrapati Rajarshi Shahu Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 354. | Shri Durgadevi Mahila Sahakari Bank Niyamith |
| 355. | Shri Gajanan Maharaj Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 356. | Shri Gajanan Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 357. | Shri Janata Sahakari Bank Limited, Halol |
| 358. | Shrikrishna Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 359. | Shri Laxmikrupa Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 360. | Shri Mahalaxmi Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 361. | Shri Mahila Sewa Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 362. | Shriram Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 363. | Shri Rajkot District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 364. | Shri Rukmini Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 365. | Shri Shivayogi Murughendra Swami Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 366. | Shri Shiveshwar Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 367. | Shri Swami Samarth Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 368. | Shri Veershaiv Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 369. | Shri Yashwant Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Kuditre (Kumbhi-Kasari) |
| 370. | Shushruti Souharda Sahakara Bank Niyamita |
| 371. | Siddheshwar Urban Co-operative Bank Maryadit |
| 372. | Sihor Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 373. | Sikar Kendriya Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 374. | Sindhudurg District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 375. | Smriti Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Mandsaur |
| 376. | Societe Generale |
| 377. | Sonbhadra Nagar Sahakari Bank |
| 378. | South Indian Bank Limited |
| 379. | Sree Charan Souhardha Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 380. | Sreenidhi Souharda Sahakari Bank Niyamitha |
| 381. | Sree Thyagaraja Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 382. | Sri Channabasavaswamy Souhardha Sahakari Bank Niyamit |
| 383. | Sri Ganapathi Urban Co-op Bank Ltd. |
| 384. | Sri Ganesh Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 385. | Sri Gokarnanath Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 386. | Sri Potti Sri Ramulu Nellore District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 387. | Sri Rama Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 388. | Sriramanagar Pattana Sahakara Bank Niyamit |
| 389. | Sri Seetharaghava Souharda Sahakara Bank Niyamitha |
| 390. | Sri Sudha Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 391. | Sri Vasavamba Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 392. | Standard Chartered Bank |
| 393. | Standard Urban Co-op. Bank (Aurangabad) Ltd. |
| 394. | Sterling Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 395. | State Bank of India#$ |
| 396. | SUCO Souharda Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 397. | Sudha Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 398. | Sumerpur Mercantile Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 399. | Sundarlal Sawji Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 400. | Surat National Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 401. | Suryoday Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 402. | Suvarnayug Sahakari Bank Ltd |
| 403. | SVC Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 404. | Swatantrya Senani Late Shripal Alase (Kaka) Kurundwad Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 405. | Tamilnad Mercantile Bank Limited |
| 406. | Tamilnadu Grama Bank |
| 407. | Tamluk-Ghatal Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 408. | Thane Bharat Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 409. | Teacher’s Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 410. | Telangana Grameena Bank |
| 411. | Telangana State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 412. | Textile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 413. | Textile Traders Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 414. | Tripura Gramin Bank |
| 415. | The Abhinav Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 416. | The Accountant General's Office Employees' Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 417. | The Adarsh Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 418. | The Adilabad District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd. |
| 419. | The Adinath Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 420. | The Agrasen Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 421. | The Agrasen Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd., Akola |
| 422. | The Ahmedabad District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 423. | The Ahmedabad Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 424. | The Ahmednagar District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 425. | The Ajara Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 426. | The Akola District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 427. | The Akola Janata Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 428. | The Akola Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 429. | The Alappuzha District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 430. | The Anand Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 431. | The Andhra Pradesh State Co-op Bank Limited |
| 432. | The Annasaheb Savant Co-Operative Urban Bank Mahad Ltd. |
| 433. | The Ambika Mahila Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 434. | The Amravati Zilla Parishad Shikshak Sahakari Bank |
| 435. | The A. P. Rajarajeswari Mahila Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 436. | The Ashta Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 437. | The Azad Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 438. | The Babasaheb Deshmukh Sahakari Bank Ltd., Atpadi |
| 439. | The Banaskantha District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 440. | The Banaskantha Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 441. | The Bangalore City Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 442. | The Bapunagar Mahila Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 443. | The Baramati Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 444. | The Bardoli Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 445. | The Baroda Central Co-op. Bank Limited |
| 446. | The Baroda City Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 447. | The Belagavi District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 448. | The Bellari District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 449. | The Bengaluru District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 450. | The Bhagyalakshmi Mahila Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 451. | The Bhagyodaya Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 452. | The Bharat Co-operative Bank (Mumbai) Limited |
| 453. | The Bharatpur Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 454. | The Bharuch District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 455. | The Bhavana Rishi Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 456. | The Bhiwani Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 457. | The Bhavnagar District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 458. | The Bhuj Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 459. | The Bicholim Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 460. | The Burdwan Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 461. | The Business Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 462. | The Calicut Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 463. | The Central Co-operative Bank Ltd., Bikaner |
| 464. | The Chanasama Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 465. | The Chandigarh State Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 466. | The Chandwad Merchant’s Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 467. | The Chembur Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 468. | The Chennai Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 469. | The Chhapi Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 470. | The Chikhli Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 471. | The Chikkamagaluru District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 472. | The Chitradurga District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd. |
| 473. | The Chittoor District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 474. | The Chitnavispura Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 475. | The Citizens Co-operative Bank Limited, Rajkot |
| 476. | The Coimbatore District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 477. | The Commercial Co-operative Bank Ltd., Jamnagar |
| 478. | The Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited, Kolhapur |
| 479. | The Co-operative Bank of Mehsana Limited |
| 480. | The Co-operative Bank of Rajkot Ltd. |
| 481. | The Cosmos Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 482. | The Cuddalore District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 483. | The Dahod Mercantile Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 484. | The Dahod Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 485. | The Darussalam Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 486. | The Davangere-Harihar Urban Sahakara Bank Niyamitha |
| 487. | The Davangere Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 488. | The Dhanbad Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 489. | The Dhanlaxmi Bank Limited |
| 490. | The Dharmapuri District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 491. | The Dindigul District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 492. | The District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd., Bidar |
| 493. | The District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd., Eluru |
| 494. | The District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd., Khammam |
| 495. | The District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd., Medak |
| 496. | The District Co-operative Central Bank, Srikakulam |
| 497. | The District Co-operative Central Bank Limited, Visakhapatnam |
| 498. | The Dombivli Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 499. | The Eenadu Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 500. | The Eluri Co-operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 501. | The Erode District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 502. | The Federal Bank Limited |
| 503. | The Financial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 504. | The Gadchiroli District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 505. | The Grain Merchants’ Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 506. | The Gandevi Peoples’s Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 507. | The Gandhidham Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 508. | The Gandhidham Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 509. | The Gandhi Gunj Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 510. | The Gandhinagar Nagarik Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 511. | The Gandhinagar Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 512. | The Goa Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 513. | The Godhra City Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 514. | The Godhra Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 515. | The Greater Bombay Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 516. | The Gujarat State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 517. | The Guntur Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 518. | The Guntur District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 519. | The Gurgaon Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 520. | The Guruvayur Co-operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 521. | The Haryana State Co-operative Apex Bank Limited |
| 522. | The Hassan District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd. |
| 523. | The Hasti Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 524. | The Himachal Pradesh State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 525. | The Honavar Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 526. | The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited (HSBC) |
| 527. | The Idar Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 528. | The Income Tax Department Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 529. | The Jain Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 530. | The Jaipur Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 531. | The Jalgaon Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 532. | The Jamkhandi Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 533. | The Jammu & Kashmir State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 534. | The Jamnagar Peoples Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 535. | The Janata Co-operative Bank Ltd., New Delhi |
| 536. | The Jhajjar Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 537. | The Jind Central Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 538. | The Junagarh Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 539. | The Junagadh Jilla Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 540. | The Kaira District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 541. | The Kaithal Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 542. | The Kakatiya Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 543. | The Kakinada Co-operative Town Bank Limited |
| 544. | The Kalupur Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 545. | The Kalyan Janata Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 546. | The Kanaka Mahalakshmi Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 547. | The Kancheepuram District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 548. | The Kangra Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 549. | The Kanyakumari District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 550. | The Karimnagar District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 551. | The Karnataka State Co-operative Apex Bank Limited |
| 552. | The Karnatak Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 553. | The Karnavati Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 554. | The Kerala State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 555. | The Khamgaon Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., Khamgaon |
| 556. | The Kodagu District Co-operative Central Bank Ltd. |
| 557. | The Kodinar Taluka Co-operative Banking Union Limited |
| 558. | The Kodungallur Town Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 559. | The Kokan Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 560. | The Kolar & Chikballapura District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 561. | The Kolhapur Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 562. | The Kollam District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 563. | The Kopargaon People's Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 564. | The Kottakkal Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 565. | The Kozhikode District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 566. | The Kranthi Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 567. | The Kukarwada Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 568. | The Kumbakonam Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 569. | The Kurukshetra Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 570. | The Lakshmi Vilas Bank Limited |
| 571. | The Latur District Central Co-op Bank Ltd. |
| 572. | The Latur Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 573. | The Lunawada People's Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 574. | The Madurai District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 575. | The Mahanagar Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 576. | The Maharaja Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 577. | The Maharashtra Mantralaya and Allied Offices Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 578. | The Maharashtra State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 579. | The Mahaveer Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 580. | The Malad Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 581. | The Mandvi Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 582. | The Mangalore Catholic Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 583. | The Mangalore Co-operative Town Bank Limited |
| 584. | The Manjeri Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 585. | The Mattancherry Sarvajanik Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 586. | The Meghalaya Co-operative Apex Bank Limited |
| 587. | The Mehsana Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 588. | The Mehsana Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 589. | The Merchants Souharda Sahakara Bank Ni., Chitradurga |
| 590. | The Modasa Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 591. | The Modern Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 592. | The Moti Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 593. | The Mudalagi Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 594. | The Mumbai Mahanagarpalika Shikshan Vibhag Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 595. | The Municipal Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 596. | The Muslim Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 597. | The Mysore & Chamarajanagar District Co-operative Central Bank Limited |
| 598. | The Nadiad People’s Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 599. | The Nainital Bank Limited |
| 600. | The Nalgonda Dist. Co-operative Central Bank Ltd. |
| 601. | The Nanded Merchant's Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 602. | The Nandura Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 603. | The Nandurbar Merchant’s Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 604. | The Naroda Nagrik Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 605. | The Nasik Merchant's Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 606. | The National Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 607. | The Naval Dockyard Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 608. | The Nav Jeevan Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 609. | The Navnirman Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 610. | The Nawanagar Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 611. | The New Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 612. | The Nileshwar Co-operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 613. | The Nilgiris District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 614. | The Ottapalam Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 615. | The Panchmahal District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 616. | The Panchsheel Mercantile Co-op. Bank Limited |
| 617. | The Panipat Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 618. | The Panipat Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 619. | The People’s Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 620. | The Pimpalgaon Merchants Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 621. | The Pioneer Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 622. | The Ponani Co-operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 623. | The Pragati Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 624. | The Pratap Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 625. | The Pudukkottai District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 626. | The Punjab State Cooperative Bank Ltd. |
| 627. | The Quilon Co-Operative Urban Bank Ltd. |
| 628. | The Raichur District Central Co-op. Bank Ltd., Raichur |
| 629. | The Railway Employee’s Co-operative Bank Ltd., Jaipur |
| 630. | The Raipur Urban Mercantile Co-op. Bank Limited, Raipur |
| 631. | The Rajajinagar Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 632. | The Rajasthan State Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 633. | The Rajasthan Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 634. | The Rajkot Commercial Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 635. | The Ramanathapuram District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 636. | The Rander People's Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 637. | The Ranuj Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 638. | The Rayat Sevak Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 639. | The Rewari Central Co-Operative Bank Ltd. |
| 640. | The Royal Bank of Scotland N.V. |
| 641. | The Sabarkantha District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 642. | The Salem District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 643. | The Sangamner Merchants Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 644. | The Sankheda Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 645. | The Santrampur Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 646. | The Sarangpur Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 647. | The Saraswat Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 648. | The Sardar Bhiladwala Pardi People’s Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 649. | The Sarvodaya Nagrik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 650. | The Sarvodaya Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 651. | The Sarvodaya Sahakari Bank Ltd., Modasa |
| 652. | The Satara District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 653. | The Satara Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 654. | The Saurashtra Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 655. | The Shahada Peoples Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 656. | The Shillong Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 657. | The Shirpur Peoples’ Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 658. | The Shoranur Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 659. | Sikkim State Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 660. | The Sirsi Urban Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 661. | The Sivagangai District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 662. | The Sonepat Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 663. | The S. S. K. Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 664. | The Sultans Battery Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 665. | The Surat District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 666. | The Surat Mercantile Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 667. | The Surat People’s Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 668. | The Sutex Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 669. | The Tamilnadu Industrial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 670. | The Tamil Nadu State Apex Cooperative Bank Limited |
| 671. | The Texco Co-operative Bank Limited, Surat |
| 672. | The Thane Janata Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 673. | The Thane District Central Co-op. Bank Ltd., Thane |
| 674. | The Thanjavur Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 675. | The Thoothukudi District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 676. | The Tiruchirapalli District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 677. | The Tirunelveli District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 678. | The Tiruvannamalai District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 679. | The Tumkur Dist. Co-op. Central Bank Ltd. |
| 680. | The Udaipur Mahila Samridhi Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 681. | The Udaipur Mahila Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 682. | The Udaipur Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 683. | The Udupi Co-operative Town Bank Limited |
| 684. | The Umreth Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 685. | The Una Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 686. | The Union Co-operative Bank Limited, Naroda |
| 687. | The Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., Dharangaon |
| 688. | The Urban Co-operative Bank Limited, Perinthalmanna |
| 689. | The Uttarsanda Peoples Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 690. | The Vaish Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 691. | The Vallabh Vidyanagar Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 692. | The Valsad District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 693. | The Varachha Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 694. | The Vellore District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 695. | The Vani Merchant’s Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 696. | The Veraval Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 697. | The Vijay Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 698. | The Vijayapura District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 699. | The Villupuram District Central Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 700. | The Virudhunagar District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 701. | The Visakhapatnam Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 702. | The Vishweshwar Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 703. | The Vyavasayik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 704. | The Warangal District Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 705. | The Washim Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., Washim |
| 706. | The West Bengal State Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 707. | The Women's Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 708. | The Yadrav Co-Operative Bank Ltd. |
| 709. | The Yamuna Nagar Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 710. | The Zoroastrian Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 711. | Thrissur District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 712. | Tirupati Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 713. | Tripura State Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 714. | Tumkur Grain Merchants Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 715. | UCO Bank |
| 716. | Ujjivan Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 717. | Uma Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 718. | Umiya Urban Co-Operative Bank Mydt. |
| 719. | Union Bank of Indiaβ |
| 720. | Unity Small Finance Bank Ltd. |
| 721. | Unjha Nagarik Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 722. | Urban Co-operative Bank Limited, Bareilly |
| 723. | Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., Siddharthnagar |
| 724. | Utkarsh Small Finance Bank Limited |
| 725. | Uttarakhand Gramin Bank |
| 726. | Uttar Pradesh Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 727. | Vaishya Nagari Sahakari Bank Limited, Parbhani |
| 728. | Vaishya Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 729. | Vaijanathappa Saraf Marathwada Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 730. | Valmiki Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 731. | Vananchal Gramin Bank |
| 732. | Vardhaman (Mahila) Co-operative Urban Bank Limited |
| 733. | Vasai Janata Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 734. | Vasai Vikas Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 735. | Vasundhara Mahila Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 736. | Veerashaiva Sahakari Bank Limited |
| 737. | Veraval People's Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 738. | Vidarbha Merchants Urban Co-op. Bank Ltd. |
| 739. | Vidyasagar Central Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 740. | Vijay Commercial Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 741. | Vikas Sahakari Bank |
| 742. | Vikas Souharda Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 743. | Vikas Urban Co-operative Bank Niyamitha |
| 744. | Vikramaditya Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 745. | Vilas Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 746. | Vima Kamgar Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 747. | Vyapari Sahakari Bank Maryadit |
| 748. | Vyaparik Audyogik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 749. | Wana Nagrik Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 750. | Warangal Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd. |
| 751. | Wardhaman Urban Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 752. | Wardha Zilla Parishad Employees (Urban) Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 753. | Wayanad District Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 754. | Woori Bank |
| 755. | Yadagiri Lakshmi Narsimha Swamy Co-operative Bank Limited |
| 756. | Yes Bank Limited |
| 757. | Yeshwant Nagari Sahakari Bank Ltd. |
| 758. | Zila Sahakari Bank Limited, Lakhimpur-Kheri |
| @ The erstwhile South Malabar Gramin Bank amalgamated with North Malabar Gramin Bank to form a new entity viz. Kerala Gramin Bank. * The erstwhile Pragathi Krishna Gramin Bank amalgamated with Kaveri Grameena Bank to form a new entity viz. Karnataka Gramin Bank. £ The erstwhile Narmada Malwa Gramin Bank amalgamated with Jhabua-Dhar Kshetriya Gramin Bank to form a new entity viz. Narmada Jhabua Gramin Bank. © The erstwhile ING Vysya Bank Limited merged with Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited. # As per the Government of India order dated February 22, 2017 regarding acquisition of State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur, State Bank of Hyderabad, State Bank of Mysore, State Bank of Patiala, State Bank of Travancore by State Bank of India, the erstwhile associate banks of SBI have merged with SBI with effect from April 1, 2017. $ As per the Government of India order dated March 20, 2017 regarding acquisition of Bharatiya Mahila Bank by State Bank of India, Bharatiya Mahila Bank has merged with SBI with effect from April 1, 2017. € The erstwhile Bihar Gramin Bank and Madhya Bihar Gramin Bank amalgamated to form a new entity viz. Dakshin Bihar Gramin Bank. ¥ The erstwhile Punjab Gramin Bank, Malwa Gramin Bank and Sutlej Gramin Bank amalgamated to form a new entity viz. Punjab Gramin Bank. ƛ The erstwhile Dena Gujarat Gramin Bank and Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank amalgamated to form a new entity viz. Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank. µ As per the Government of India Gazette Notification dated January 02, 2019, Vijaya Bank and Dena Bank amalgamated with the Bank of Baroda with effect from April 01, 2019. α As per the Government of India Gazette Notification dated March 4, 2020, Oriental Bank of Commerce and United Bank of India amalgamated with Punjab National Bank with effect from April 01, 2020. β As per the Government of India Gazette Notification dated March 4, 2020, Andhra Bank and Corporation Bank amalgamated with Union Bank of India with effect from April 01, 2020. Ω As per the Government of India Gazette Notification dated March 4, 2020, Syndicate Bank amalgamated with Canara Bank with effect from April 01, 2020. ℼ As per the Government of India Gazette Notification dated March 4, 2020, Allahabad Bank amalgamated into Indian Bank with effect from April 01, 2020. |
|
National Electronics Funds Transfer
Customer Facilitation Centres for NEFT & RTGS
Customer Facilitation Centres - NEFT
| Customer Facilitation Centres – NEFT (Updated as on August 14, 2023) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| S No | BANK NAME | PHONE | E Mail |
| 1 | ABHYUDAYA COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-25260172 | neftcell@abhyudayabank.net |
| 2 | AHMEDABAD MERCANTILE COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 079-26426582-84-88 | treasury@amco-bank.com |
| 3 | AHMEDNAGAR MERCHANTS CO-OP BANK LTD | Tel: 9767477700 | admin@amcbank.in; suresh.katariya@rediffmail.com |
| 4 | AIRTEL PAYMENTS BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0124-4247797 | nefthelpdesk@airtelbank.com |
| 5 | AKOLA JANATA COMMERCIAL COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 0724-2430012/ 2430241/2430639 | rtgsneftops@akolajanatabank.com |
| 6 | ALMORA URBAN COOPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 05946-286300; 05962-231947; 05962-230743 | rtgs.aucb@almoraurbanbank.com info@almoraurbanbank.com |
| 7 | AMBARNATH JAI HIND CO -OP BANK LTD | Tel: 0251 2605068/2605069/2600696 | rtgs@jaihindbank.com; jaihindbank@gmail.com |
| 8 | ANDHRA PRADESH GRAMEEN VIKAS BANK | Tel: 7382620369, 9490153763, 9440903904, 9491065590 | treasury@apgvbank.in; cmaccounts@apgvbank.in; cmit@apgvbank.in |
| 9 | ANDHRA PRAGATHI GRAMEENA BANK | Tel: 7382633823 | rtgsneft@apgb.in |
| 10 | APNA SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-24103313 | cpd@apnabank.co.in, |
| 11 | AU SMALL FINANCE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 9116181332/ 7340011989/ 9116181708 | rtgsneft@aubank.in; epay@aubank.in |
| 12 | AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND BANKING GROUP LIMITED | Tel: 022 4112 0073 | indiapcomumbaioffice@anz.com pgsupport.india@anz.com |
| 13 | AXIS BANK | Tel: 022 - 24253491 /3492 / 3493 | cfc@axisbank.com |
| 14 | B N P PARIBAS | Tel: 022- 61964645 / 4646 / 4640 / 4642 | cms.payments@asia.bnpparibas.com |
| 15 | BANDHAN BANK LIMITED | Tel: 033-40456456 Ext: 5415 |
rtgsneft.desk@bandhanbank.com |
| 16 | BANK OF AMERICA | Tel: 044-42904526/4711/4527/4525 | dg.payments_chennai@bofa.com |
| 17 | BANK OF BAHARAIN AND KUWAIT BSC | Tel: 022-22880038 / 22823698 / 99 Extn - 246/238 | csdmumbai@bbkindia.com |
| 18 | BANK OF BARODA | Tel: 0265-2316160/6161 | neft.mumbai@bankofbaroda.com |
| 19 | BANK OF CEYLON | Tel: 044-39519907/9902, 044-28190972 | bocops@bankofceylon.in |
| 20 | BANK OF INDIA | Tel: 022-61312997 | boi.neft@bankofindia.co.in |
| 21 | BANK OF MAHARASHTRA | Tel: 020 2450 4005/ 4006 | bomneft@mahabank.co.in |
| 22 | MUFG Bank, Ltd. | Tel: 011-41003456 /220 /275 /453 /464 | ndledp@vsnl.net.in |
| 23 | BARCLAYS BANK | Tel: 022-61754261 / 4619 / 4620 / 4670 | grcbpayment.ops@barclays.com |
| 24 | Bassein Catholic Co-op Bank Ltd | +91-8888837146 | rtgs@bccb.co.in |
| 25 | BHAGINI NIVEDITA SAHAKARI BANK LTD | Tel: 020-25479707/25479708, 9822034166 020-25447619/25447620 |
neft_rtgs@bhagininiveditabank.com, madhura.karve@bhagininiveditabank.com, ho@bhagininiveditabank.com |
| 26 | BHARAT COOPERATIVE BANK MUMBAI LIMITED | Tel: 022-61890106/ 107 | payments@bharatbank.co.in |
| 27 | Canara Bank | Tel: 080-25129486/87/88/89 080-25129496 |
horeconhelpdesk@canarabank.com neft@canarabank.com |
| 28 | CAPITAL SMALL FINANCE BANK LTD. | Tel: 0181-5050759/727/730/775 | epayments@capitalbank.co.in treasury@capitalbank.co.in |
| 29 | CSB BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0484-6615504/ 05, 9072601527/ 528 |
rtgs@csb.co.in |
| 30 | CENTRAL BANK OF INDIA | Tel: 022-22637966 | cbineftcfc@centralbank.co.in |
| 31 | CHINATRUST COMMERCIAL BANK LIMITED | Tel: 011-43688888 , 233560001 | in.customerservices@ctbcbank.com |
| 32 | CITI BANK | Tel: 022 6132 8761; 022 6132 8891; 022 6132 8570 |
pay.ops@citi.com India.citiservice@citi.com paylink.rtgs@imcap.ap.ssmb.com rtgs.citi@citi.com |
| 33 | CITIZEN CREDIT COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-22658969 | neft.rtgs@citizencreditbank.com; cm.cpd@citizencreditbank.com; agm3@citizencreditbank.com; dgm3@citizencreditbank.com |
| 34 | CITY UNION BANK LIMITED | Tel: 044-28297905 | payment_system@cityunionbank.in |
| 35 | CREDIT AGRICOLE CORPORATE AND INVESTMENT BANK CALYON BANK | Tel: 022-67371030/1031 | rtgs.crly@ca-cib.com |
| 36 | CREDIT SUISSE AG | Tel: 022 6777 3417022 6777 3510 | list.rtgs.cres@credit-suisse.com |
| 37 | DARUSSALAM CO-OPERATIVE URBAN BANK LTD | 040-24805176 / 8125108125 | dcub1000@darussalambank.com; dcub_ho@darussalambank.com |
| 38 | DCB BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-66187225/228/244/243/283/246/021 | neft@dcbbank.com |
| 39 | DEOGIRI NAGARI SAHAKARI BANK LTD | Tel: 0240-2240212/2484827/28 | neftrtgs@deogiribank.com |
| 40 | DEPOSIT INSURANCE AND CREDIT GUARANTEE CORPORATION | Tel: 022-23062680, 23084121 | dicgccsd@rbi.org.in |
| 41 | DEUTSCHE BANK | Tel: 022-71806411, 022-71803524, 022-71806318, 022-71803918 | neft.deutsche@db.com / rtgs.deutsche@db.com |
| 42 | DBS BANK INDIA LTD. | Tel: 022 – 6833 0934 | paymentrecall@dbs.com |
| 43 | DHANALAKSHMI BANK | Tel: 0487-6627046 / 084 | neft@dhanbank.co.in, rtgs.dlxb@dhanbank.co.in, rtgs@dhanbank.co.in |
| 44 | DMK JAOLI BANK LTD | Tel: 022-23828488 | jsbl@vsnl.com; hoaccounts@jaolibank.in |
| 45 | DOHA BANK QPSC | 022-6286 1161, 022-6286 1162, 022-6286 1186 |
indiahelpdesk@dohabank.co.in |
| 46 | DOMBIVLI NAGARI SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0251-2875000-9, 0251-2875077/78/79 | info@dnsb.co.in |
| 47 | DURGAPUR STEEL PEOPLES COOPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 0343 - 2575711, 9475413151 8373090004 |
clearingcell@dspcoopbank.com dspcoop@gmail.com; chanchal.pal@dspcoopbank.com |
| 48 | EMIRATES NBD BANK PJSC | Tel: 8879020254 | rtgsebil@EmiratesNBD.com |
| 49 | EQUITAS SMALL FINANCE BANK | Tel: 044-30898048/8068/8015/8056 | rtgs-cell@equitasbank.com |
| 50 | ESAF SMALL FINANCE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0487 - 2373290, 9072604056,8589975585,8589933364,9072600833 | payments@esafbank.com; nitha.kannan@esafbank.com; aby.abraham@esafbank.com; binumon.k@esafbank.com |
| 51 | EXPORT IMPORT BANK OF INDIA | Tel: 022-22172669/2647/2438/2444 | rtgs@eximbankindia.in |
| 52 | FEDERAL BANK | Tel: 0484-2752051, 2752077 | neft@federalbank.co.in |
| 53 | FINCARE SMALL FINANCE BANK | Tel: 080 - 42504444 Ext 643, 611, 610 | cpcpayments@fincarebank.com |
| 54 | FINO PAYMENTS BANK LTD | Tel: 022-71047116, 022-71047025, 022- 71047191 | neftrtgs.cell@finobank.com, care@finobank.com, customercare@finobank.com |
| 55 | FIRST ABU DHABI BANK PJSC | Tel: 022-33311131/1151 | mumbaisupportit@nbad.com |
| 56 | FIRSTRAND BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-66258682/ 66258666/ 66258629 | frin.tradeoperations@firstrand.co.in |
| 57 | G P PARSIK BANK | Tel: 022-25456500, Extn. 6529, 6509 | invest@gpparsikbank.com; accounts@gpparsikbank.net |
| 58 | GS MAHANAGAR COOPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 022- 24710952 / 24710962 / 24710821 | edpmanager@mahanagarbank.com |
| 59 | HARYANA STATE CO-OP APEX BANK | Tel: 0172-2784278 | harco17@gmail.com; neft@harcobank.org.in; rtgs@harcobank.org.in |
| 60 | HDFC BANK LTD | Tel: 022-30752044 / 53 | neftoutward@hdfcbank.com; neftinward@hdfcbank.com |
| 61 | HIMACHAL PRADESH STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 0177-2659641 | rtgs.hpsc@hpscb.com |
| 62 | HSBC BANK | Tel: 022-45053307, 61223370 | paymentinvestigations@hsbc.co.in |
| 63 | HUTATMA SAHAKARI BANK LTD WALWA | 0231-2664025/ 26 | ITCELL@HUTATMABANK.COM; HO@HUTATMABANK.COM |
| 64 | ICICI BANK LTD | Tel: 022- 33667777 & 040- 33667777 Fax: 040-41064450 |
neft.query@icicibank.com |
| 65 | IDBI BANK | Tel : 022 – 66552776/77/78, 022-66700304 022-66908536 |
etpc@idbi.co.in; rtgsneftops@idbi.co.in |
| 66 | IDFC FIRST BANK | Tel: 49850059/58/55/56/61 | cfc@idfcfirstbank.com neftcell@idfcfirstbank.com |
| 67 | IDUKKI DISTRICT CO OPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 04862 – 235141 | it@idukkidcb.in |
| 68 | INDIA POST PAYMENTS BANK LIMITED | Tel: 011-23815485, 23815488 | rtgs.cfc@ippbonline.in |
| 69 | Indian Bank | 044-28294988 044-28134173 |
rtgscell@indianbank.co.in |
| 70 | INDIAN OVERSEAS BANK | Tel: 044-28584896, 28889397 | rtgscell@iobnet.co.in |
| 71 | INDUSIND BANK | Tel: 022-42271639/40/41/42, 022-62815131/ 5123 | neft@indusind.com |
| 72 | INDUSTRIAL AND COMMERCIAL BANK OF CHINA LIMITED | Tel: 022-33155931/5926 | rtgs.icbk@india.icbc.com.cn |
| 73 | INDUSTRIAL BANK OF KOREA | Tel: 011-40768000 / 8022 / 8009 | neft.ibko@ibk.co.kr ibkamitdeb@ibk.co.kr rohit@ibk.co.kr |
| 74 | IRINJALAKUDA TOWN CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 9447755843, 9497068429, 9847411160, 0480-2670300, 2670331 | ho@itubank.com, mail@itubank.com |
| 75 | JALGAON JANATA SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0257-2235534/2234794 | jjsbrtgs@gmail.com |
| 76 | JAMMU AND KASHMIR BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0194-2481930/31/32/33/34/35 | neftservices@jkbmail.com; jakaneft@jkbmail.com |
| 77 | JANA SMALL FINANCE BANK | Tel: 080-33425262/Ext:358/143 | channel_payments@janabank.com |
| 78 | JANASEVA SAHAKARI BANK BORIVLI LIMITED | Tel : 022- 28914747, 28333522 | jssbl@mtnl.net.in |
| 79 | JANASEVA SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 020-24440097 | investment@janasevabankpune.com |
| 80 | JANATA SAHAKARI BANK LTD, PUNE | Tel: 020 24521092020 24521093Mobile: 9970013148 | jsbservice@janatabankpune.com |
| 81 | JANKALYAN SAHAKARI BANK | Tel: 022-25222582/ 25246804, 022-25264123/122/151/111 | jksbl@jksbl.com |
| 82 | JIO PAYMENTS BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-35554097 | rajesh3.gupta@ril.com |
| 83 | JP MORGAN CHASE BANK | Tel:- 022-61575043, 022 61573844, 022 61573837 Tel:- 022 61573305 / 61573445 / 61573667 |
mumbai.cash.operation@jpmorgan.com funding.mumbai.branch@jpmorgan.com rtgs_chas@jpmorgan.com |
| 84 | KALLAPPANNA AWADE ICHALKARANJI JANATA SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0230-2427263 | treasury@ijsbank.com |
| 85 | KALUPUR COMMERCIAL COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 079-27582020 to 27582026 | info@kalupurbank.com rtgs.kccb@kalupurbank.com |
| 86 | KALYAN JANATA SAHAKARI BANK | Tel: 0251-2219009 / 9030 / 9024 | kjsbrtgs@kalyanjanata.in |
| 87 | KARNATAKA BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022 - 22823031/32 | neft.srbr@ktkbank.com |
| 88 | KARNATAKA VIKAS GRAMEENA BANK | Tel: 0836-2442204 | kvgbhoit@gmail.com neftrtgscell@kvgbank.com |
| 89 | KOOKMIN BANK | 124-4532222 | ravish.arora@kbfg.com sheenu.chawla@kbfg.com ravish.dutta@kbfg.com |
| 90 | THE KARUR VYSYA BANK LTD | Tel: 0422–2227778, 0422–2227779, 0422-2227760 | neft@kvbmail.com; neftcfc@kvbmail.com |
| 91 | KEB HANA BANK | Tel: 044-49056320/6305 | kebchennai@hanafn.com |
| 92 | KERALA GRAMIN BANK | Tel: 0497-2704810 | neftcell.kgb@keralagbank.com |
| 93 | KOTAK MAHINDRA BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-6605 6597 / 98 / 99 | neftrtgs.query@kotak.com |
| 94 | KOZHIKODE DISTRICT COOP BANK LTD. | Tel: 0495-2701520 | rtgs@kdcbank.com |
| 95 | MAHARASHTRA GRAMIN BANK | Tel: 0240-2476141, 022-25435154, 25344059/60 |
rtgs@mahagramin.co.in neft@mahagramin.co.in mgbneftcell@gmail.com |
| 96 | MAHARASHTRA STATE COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 022 22800653/654, 22822216 | paymentcell@mscbank.com; rtgs@mscbank.com |
| 97 | MAHESH SAHAKARI BANK LTD PUNE | Tel: 8446113097 & 7720932223 | accounts@maheshbankpune.in |
| 98 | MASHREQBANK PSC | Tel: 022-66327200/300/301 | opsindia@mashreq.com; |
| 99 | MIZUHO BANK LTD. | Tel: 022 49112000/21/23/61 022 49112746/77 | inward.remittances@mizuho-cb.com |
| 100 | MODEL CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 022-66914227/ 8080938018 | rtgs@modelbank.in |
| 101 | NABARD | Tel: 9321966445 (022-26539793) |
fd.disb@nabard.org |
| 102 | NAGAR URBAN CO OPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 0241-2346941, 2343642 | rtgs@nagarurbanbank.com |
| 103 | NAGPUR NAGARIK SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0712-2764313 ,2761386 | neft@nnsbank.com |
| 104 | NEW INDIA CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 022 6626 4353 | rtgsdesk@newindiabank.in / rtgs.nicb@newindiabank.in |
| 105 | NKGSB COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-67545022,67545009 | rtgs@nkgsb-bank.com |
| 106 | NORTH EAST SMALL FINANCE BANK | Tel: 0361-7180001 | customercare@nesfb.com |
| 107 | NSDL Payment Bank Ltd | Tel: 022-42022100 | care@nsdlbank.co.in nspboperations@nsdlbank.co.in |
| 108 | NUTAN NAGARIK SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 079-26445229 | rtgs@nutanbank.com |
| 109 | PAYTM PAYMENTS BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0120-4456456 | neftrtgs.support@paytmbank.com |
| 110 | KARNATAKA GRAMIN BANK | 08194-234315, 08194-234215 | hoanx.neftcell@kgbk.in; dbswing.kgbk@kgbk.in |
| 111 | PRIME CO-OP. BANK LTD. | Tel: 0261 - 2804777 | rtgs@primebankindia.com |
| 112 | PT BANK MAYBANK INDONESIA TBK | Tel: 022-67303422/3423 | rtgs.ibbk@maybank.co.in |
| 113 | PUNJAB AND MAHARSHTRA COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 022-61284316/4317/4313 | rtgs@pmcbank.com |
| 114 | PUNJAB AND SIND BANK | Tel: 011-25860657,25826216 | b0385@psb.co.in; rtgs@psb.co.in |
| 115 | PUNJAB NATIONAL BANK | Tel: 022-22627511 | neft@pnb.co.in |
| 116 | QATAR NATIONAL BANK (Q.P.S.C.) | Tel: 022-62296306/ 6311 | indiaoperations@qnb.com |
| 117 | RABOBANK INTERNATIONAL | Tel: 022-22097890/7900/7881 | fm.in.mumbai.cmps@rabobank.com |
| 118 | RAJARAMBAPU SAHAKARI BANK | Tel: 9890080260 | account@rajarambapubank.org; |
| 119 | RAJARSHI SHAHU SAHAKARI BANK Ltd | 020-24432557, 020-24435384, 020-24435385 |
rtgsneft@rajarshishahubankpune.com |
| 120 | RAJGURUNAGAR SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel : 02135- 222085,222118 | rtgs.rsbl@rajgurunagarbank.com |
| 121 | RAJKOT NAGARIK SAHAKARI BANK LTD. | Tel: 0281-2238524, 2226476, 2222054 | rtgsops@rnsbindia.com, rtgs@rnsbindia.com, |
| 122 | RBL BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022- 48829025 to 42 | rtgsneftoperation@rblbank.com |
| 123 | RESERVE BANK OF INDIA (FOR GOVT BANKING DIVISION) | Tel: 022-22603329 | neftpadmumbai@rbi.org.in |
| 124 | SAHEBRAO DESHMUKH COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel : 022-28522514/15, 022-28520369 | clg@sdcbank.in |
| 125 | SAMARTH SAHAKARI BANK LTD. | Tel: 02172744214 | rtgs.sbls@samarthbank.com |
| 126 | SARASWAT COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | (022) 67315444, 67315402 | rtgs_neft@saraswatbank.com; suhas.shidhaye@saraswatbank.com |
| 127 | SBER BANK | Tel: 011-40048888, 40048886, 40048887 | u.bhatnagar@sberbank.co.in |
| 128 | SBM BANK MAURITIUS LIMITED | Tel: 022-43028888/801/802 | csdmumbai@sbm-india.com |
| 129 | SHIKSHAK SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0712-2722705 / 2774866 | rtgs.sksb@shikshakbank.com |
| 130 | SHINHAN BANK | Tel: 022-61992000 | operations.mum@shinhan.com; patra@shinhan.com; treasury.bo.ind@shinhan.com; rtgs.shbk@shinhan.com |
| 131 | SHIVALIK SMALL FINANCE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0132-2726125 0132-2726147 |
rtgs@shivalikbank.com |
| 132 | SHRI CHHATRAPATI RAJASHRI SHAHU URBAN COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel - 2442-229772, 2442-228961 | headoffice@shahubank.com |
| 133 | SHRI VEERSHAIV CO-OP BANK LTD | Tel: 0231-2536940, 8380051173 | nitincharankar@shriveershaivbank.com |
| 134 | SINDHUDURG DCCB LTD | Tel: 02362-229005 To 10 | rtgs.neft@sindhudurgdcc.com |
| 135 | SIR M. VISVESWARAYA CO-OP BANK LTD. | Tel: 9480885371, 9449599908 | hl.suresh@yahoo.co.in; l.ganesh@vcb.co.in |
| 136 | SOCIETE GENERALE | Tel: 022-66309500 | mum.oper.mop@socgen.com |
| 137 | SOLAPUR JANATA SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel – 0217-2741100 | info@sjsbbank.com |
| 138 | SOUTH INDIAN BANK | 0484 2556003, 080 28543444. | rtgscell@sib.co.in rtgscell1@sib.co.in |
| 139 | STANDARD CHARTERED BANK | Tel: 044-674-41156 / 044-674-41251 | neft.recall@sc.com |
| 140 | STATE BANK OF INDIA | Tel: 022-2756 0743 / 022-2756 0746 | neft@sbi.co.in |
| 141 | SUMITOMO MITSUI BANKING CORPORATION | Tel: 011-47689111 | rtgs_smbc@in.smbc.co.jp |
| 142 | SURAT NATIONAL COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0261-2464 621 to 624 | rtgs.sunb@sncb.in |
| 143 | SURYODAY SMALL FINANCE BANK LTD | Tel: 022-41856734/40436757 | payments@suryodaybank.com |
| 144 | SUCO SOUHARDHA SAHAKARI BANK LTD. | Tel: 08392-255201/08392-254104/ 08392-297296 | neft.suco@sucobank.com rtgs.suco@sucobank.com |
| 145 | THE SUTEX COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0261-2632519, 2632027/28 | rtgs.support@sutexbank.in |
| 146 | TAMILNAD MERCANTILE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 044-28131092/28131091 | rtgs@tmbank.in |
| 147 | Telangana State Co-Op Apex Bank | Tel: 040-23443814/ 24685501, 040-24685568, 040-23443845 | rtgscell@tscab.org |
| 148 | TEXTILE TRADERS COOP BANK LTD. | Tel : 079-26430545079-26434255 / 26434200 | rtgs.ttcb@ttcbank.co.in headoffice@ttcbank.co.in |
| 149 | THE A.P. MAHESH COOPERATIVE URBAN BANK LIMITED | Tel: 040- 24732711/22 | info@apmaheshbank.com; hofin@apmaheshbank.com |
| 150 | THE AKOLA DISTRICT CENTRAL CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD, AKOLA | Tel: 0724-2415107, 0724-2415108, 18002332393 | rtgs.adcc@akoladccbank.com |
| 151 | THE ANDHRA PRADESH STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 040-27687417/568/579 | rtgscell@apcob.org |
| 152 | THE BANK OF NOVA SCOTIA | Tel: 022-6636 4200 | support.mumbai@scotiabank.com |
| 153 | THE BARAMATI SAHAKARI BANK | Tel: 02112-224865 Ext : 316 | rtgs@baramatibank.com |
| 154 | THE COSMOS CO OPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-2447 6043 / 44, 022-2447 4278 | neftcell@cosmosbank.in |
| 155 | THE DELHI STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | 011-41705038 011-23281924 |
bkg.dscb@gmail.com, banking@dscb.in dscbrtgs2014@gmail.com |
| 156 | THE GADCHIROLI DISTRICT CENTRAL COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 07132-232050,232965, 233438,233570, 8055143754 (Pravin Janganwar) | gdcc_gad@gdccbank.com |
| 157 | THE GREATER BOMBAY COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022 61285927/61285900 | clearing@greaterbank.com |
| 158 | THE GUJARAT STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 079-27459013, 27459916, 27459033 | info@gscbank.coop |
| 159 | THE HASTI COOP BANK LTD | Tel: 02566-245616, 247306, 244106, 244306, 247306, 247307 | rbiusersgroup@hastibank.org |
| 160 | THE JALGAON PEOPELS COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0257-2227711 to16 | rtgs.jpcb@jpcbank.com |
| 161 | The Kangra Central Co-Op Bank Ltd | Tel: 01892-222269 Ext. 268 | dbdc@kccb.in |
| 162 | THE KANGRA COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 011-23582056 | ser_branch@kangrabank.com |
| 163 | THE KARAD URBAN COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-24171471 | treasury@karadurbanbank.com |
| 164 | THE KARANATAKA STATE COOPERATIVE APEX BANK LIMITED | Tel: 080-22976614 | rtgs@karnatakaapex.com |
| 165 | THE KURMANCHAL NAGAR SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 05942-263574 | kurmanchalbank@yahoo.com |
| 166 | THE MEHSANA URBAN COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 02762-240761 | info@mucbank.com |
| 167 | THE MUMBAI DISTRICT CENTRAL COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-22616911/12 | neft@mumbaidistrictbank.com |
| 168 | THE MUNICIPAL COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022- 22616911/12 | accounts@mcbmumbai.com |
| 169 | THE NAINITAL BANK LIMITED | Tel: 011-23583041/40 | rtgshelpdesk@nainitalbank.co.in |
| 170 | THE NASIK MERCHANTS COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0253-2308210 /0253-2308213 | rtgsneft@namcobank.in; helpdesk@namcobank.in; cto@namcobank.in |
| 171 | THE NAVNIRMAN CO OP BANK LTD. | Tel: 079-26568259 079-26568258 | support@navnirmanbank.com |
| 172 | THE PANDHARPUR URBAN CO OP. BANK LTD. PANDHARPUR | Tel: 02186-228484, 223163, 223484 | rtgsneft@pandharpurbank.com |
| 173 | THE RAJASTHAN STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0141-2744704 | rscb.raj@gmail.com |
| 174 | THE SEVA VIKAS COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 020-27412289, 020-27413371 | rtgs.svbl@sevavikasbank.com |
| 175 | THE SHAMRAO VITHAL CO OP BANK | Tel: 022-71991468-75 | rtgscell@svcbank.com |
| 176 | THE SURAT DISTRICT CO-OP BANK LTD. | Tel: 0261-2466012, 0261-2466018 | agmbanking@sudicobank.com; treasury@sudicobank.com |
| 177 | THE SURATH PEOPLES COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0261-2464621 to 624 | info@spcbl.in |
| 178 | THE TAMIL NADU STATE APEX COOPERATIVE BANK | Tel: 044-25358859/2308, 044-25340973 | rtgs@tnscbank.com |
| 179 | THE THANE BHARAT SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-25404747/50/51 | rtgs.tbsb@thanebharatbank.net; rtgs.tbsb@tbsbl.com |
| 180 | THE THANE DISTRICT CENTRAL COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-25433510 | edp@thanedistrictbank.com |
| 181 | THE UDAIPUR URBAN CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 8279128886 | addlceo@uucbudaipur.com |
| 182 | THE VARACHHA COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0261-4008146/47 | nefthelpdesk@varachhabank.com |
| 183 | THE VISHWESHWAR SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 020-24271397, 020-24261755/2745 | treasury@vishweshwarbank.com |
| 184 | THE WEST BENGAL STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 033 4004 2721, 4000 0386 | infoneft@wbstcb.com |
| 185 | THE ZOROASTRIAN COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-22696050 | rtgs.zcbl@zcbl.in |
| 186 | THRISSUR DISTRICT COOPERATIVE BANK LTD | 04872329520 | neftrtgs@thrissurdcb.com |
| 187 | TJSB SAHAKARI BANK LTD | Tel: 022-25838527 | rtgs.tjsb@tjsb.co.in |
| 188 | TUMKUR GRAIN MERCHANTS COOPERATIVE BANK LIMITED | Tel : 0816-4021102/03, 0816-2257636 | rtgs.tgmb@tgmcbank.com |
| 189 | UCB PERINTHALMANNA | Tel: 9447077586, 9447326689, 9447404902 | info@ucbpmna.com; ucbpchiefacct@gmail.com; ucbpagm@gmal.com |
| 190 | UCO BANK | Tel: 022-66547342,7343,7344 & 7359 | rtgsneftcell@ucobank.co.in |
| 191 | UJJIVAN SMALL FINANCE BANK | Tel: 080 40712193 | ujjivan-neft@ujjivan.com |
| 192 | UNION BANK OF INDIA | Tel: 022 22896510 / 6587 | neftcell@unionbankofindia.com |
| 193 | UNITED OVERSEAS BANK LIMITED | Tel: 022-42472814/11/12/15 | uob.mumbai@uobgroup.com |
| 194 | UTKARSH SMALL FINANCE BANK LTD | Tel: 1800-123-9878 | customercare@utkarsh.bank |
| 195 | VASAI JANATA SAHAKARI BANK | Tel: 0250 2308898/2308327; Mobile:7774038963; 8879001410 |
s.thakare@vjsbl.com; dc@vjsbl.com neft-rtgs@vjsbl.com martin.sequeira@vjsbl.com |
| 196 | VASAI VIKAS SAHAKARI BANK LIMITED | Tel: 0250-2326998, 0250-2326984 | rtgs@vasaivikasbank.co.in |
| 197 | WOORI BANK | Tel: 044-33466952 | rtgs.hvbk@wooribank.com |
| 198 | YES BANK | Tel: 18001200, 022-68547571, 022-50229981, 022-68548087 |
yestouch@yesbank.in; cfc@yesbank.in |
| 199 | SANT SOPANKAKA SAHAKARI BANK LTD. | Tel: 020-24444001 020-24444002 Mobile: 9763723710 |
rtgsneft@santsopankakabank.com; ad_gaikwad@santsopankakabank.com; am_gavali@santsopankakabank.com; sachin_jagtap@santsopankakabank.com; vs_pawar@santsopankakabank.com; edp@santsopankakabank.com; sp_ghare@santsopankakabank.com; vikas_jagtap@sopankakabank.com; an_shinde@santsopankakabank.com; dm_sabne@sopankakabank.com |
| 200 | ZILA SAHAKRI BANK LIMITED GHAZIABAD | Tel: 0120-2824884/85/86, 0120-2823955 | rtgs.zsbl@zsblghaziabad.com |
| 201 | NAVJEEVAN CO-OP. BANK LTD. | Tel: 0251-2572101 | navjeevanbank@njcb.in |
| 202 | VIJAY COOPERATIVE BANK | 079-26587011 079-26581960 079-26580750 |
edp@vijaycooperativebank.com; agm@vijaycooperativebank.com |
| 203 | KERALA STATE CO-OPERATIVE BANK | 0471-2547252, 0471-2547249 | kscb@keralacobank.com; cobankcad@yahoo.co.in |
| 204 | Nilambur co –operative bank ltd | Hareesh VS: 9961766976 Rajeev R Nair: 9495762810 |
hareeshvs@nilamburcub.com; rajeevrnair@nilamburcub.com |
| 205 | Rajasthan Marudhara Gramin bank | Gaurav Agrawal : 7073454003 Gyan Prakash Gupta : 7073454371 |
psg@rmgb.in fac@rmgb.in |
| 206 | Saraspur Nagarik Co – Operative Bank | Dhaval Patel: 9727845001 Vishal Mistry: 9898177066 Ankur Patel: 9662625065 |
info@saraspurbank.com sncbank@gmail.com neftrtgssncbank@gmail.com |
| 207 | MALKAPUR URBAN CO-OP BANK LTD. | Tel: 9422207012 Rajesh Bapat(Asst. Manager) | bapatmlk@rediffmail.com |
| 208 | AJARA URBAN CO-OP BANK LTD. | Tel: 0232-3246084/ 8007030197/ 7798960981 |
headit@ajarabank.com; rtgs.rbi@ajarabank.com |
| 209 | UTTAR PRADESH CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD | Tel: 0522-4151200 Ext-402 2623806, 2623740Mobile: 7525006048 |
rtgshelpdesk@upcbl.in itcell@upcbl.in |
| 210 | MUSLIM COOPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 020 – 26435007/ 020 - 24475215 / 24473521 |
nazimmulla72@gmail.com 0502ruby@gmail.com ahmed@muslimcooperativebank.com |
| 211 | ODISHA STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 0674-2375100/2510528 | oscb.cbs2013@gmail.com |
| 212 | SATARA SAHAKARI BANK LTD | Tel: 8108479999, 022-24124743, 022-24146371 |
rtgsneft@satarabank.net, info@satarabank.net |
| 213 | PUSAD URBAN COOPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 0712-2292644, 7888097938 | ho@pucbl.org, rtgs@pucbl.org, nagpur@pucbl.org |
| 214 | COASTAL LOCAL AREA BANK LTD | 0866-2494425/26 | rtgs.neft@coastalareabank.com |
| 215 | THE PUNJAB STATE COOPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 0172-5067016 | neftrtgs@pscb.in |
| 216 | THE NAWANAGAR CO-OPERATIVE BANK LTD. | Tel: 0288-2563984/85 | rtgsneftops@nawanagarbank.co.in |
| 217 | ARVIND SAHAKARI BANK LTD. | Tel: 9860304002, 9860361472, 9765861919 | asbl_ho@arvindbank.com ravi.harjal@arvindbank.com yogesh.wankhede@arvindbank.com vaishali.moundekar@arvindbank.com |
| 218 | Sree Charan Souhardha Co-operative Bank Ltd | 080 - 26676837 080 - 26606836 +91 9901453378 +91 9901453385 |
manager.accounts@sreecharanbank.com it.support@sreecharanbank.com it.head@sreecharanbank.com |
| 219 | Janatha Seva Co-operative Bank Ltd. | 080-29776055, 080-23504924, 080-23110019, 9980846055 |
jscbneftcell@jscbl.com jscbrtgscell@jscbl.com girishbg@jscbl.com yogesh.b@jscbl.com geetha.c@jscbl.com |
| 220 | Bombay Mercantile Co-operative Bank Ltd. | 022-23019825 | cfc@bmcbank.co.in |
| 221 | Jila Sahakari Kendriya Bank Maryadit Rajnandgaon | 07744-223620, 220409, 224408 |
cbs@jskbrjn.com, account@jskbrjn.com, jskbrajnandgaon@jskbrjn.com |
| 222 | The Banaskantha Mercantile Co-Operative Bank Ltd. | 02742-253849 7573031002 |
rtgsdesk@bmcbbank.com; admin@bmcbbank.com |
| 223 | The Satara District Central Co-Op Bank Ltd. | 02162-236036 | rtgsneft@sataradccb.com |
| 224 | The Malad Sahakari Bank Ltd. | 022-7506444054/55, 022-28838636, 022-28889898 |
accounts@maladbank.com it@maladbank.com |
| 225 | The Akola Urban Co-operative Bank Ltd., Akola | 0724-2453851 | rtgs@aucbakola.com |
| 226 | Smriti Nagrik Sahakari Bank Maryadit, Mandsaur | 07422-405622 | smritibank@smritibank.com |
| 227 | Pavana Sahakari Bank Ltd Pune | 020-67171600 020-67171601 |
neftrtgs@pavanabank.com |
| 228 | Chhattisgarh Rajya Gramin Bank | 0771-4388819 | psg@cgbank.in |
| 229 | The Meghalaya Co-Operative Apex Bank Ltd. | 0364-2224160 0364-2226169 |
headoffice@megcab.com |
| 230 | Shree Kadi Nagarik Sahakari Bank Ltd. | 02764-263500, 9904997770, 8511074025 |
it@knsb.in; info@knsb.in; support@knsb.in |
| 231 | Saurashtra Gramin Bank | 0281-2482422 | neft-rtgs_support@sgbrrb.org |
| 232 | Unity Small Finance Bank Limited | 022-42159421 / 557 | payments@unitybank.co.in |
| 233 | The Burdwan Central Cooperative Bank Ltd | 8373077670, 8373099601, 8373077636 |
rtgs@burdwanccb.in; hofund@burdwanccb.in |
Guidelines for the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS)
| Guidelines for the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS) |
|---|
|
(Updated as on July 2, 2018) Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), despite the important role played by them in the economic fabric of the country, continue to face constraints in obtaining adequate finance, particularly in terms of their ability to convert their trade receivables into liquid funds. In order to address this pan-India issue through setting up of an institutional mechanism for financing trade receivables, the Reserve Bank of India had published a concept paper on “Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) Factoring-Trade Receivables Exchange” in March 2014. 2. Based on the public comments received on the concept paper and the subsequent draft guidelines issued for setting up and operating the system, and interactions held with relevant stakeholders, the following guidelines are being issued for setting up and operating the trade receivables system in the country. These Guidelines are issued by Reserve Bank of India under Section 10(2) read with Section 18 of Payment & Settlement Systems Act, 2007 (Act 51 of 2007). Scheme 3. The scheme for setting up and operating the institutional mechanism for facilitating the financing of trade receivables of MSMEs from corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), through multiple financiers will be known as Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS). 4. The TReDS will facilitate the discounting of both invoices as well as bills of exchange. Further, as the underlying entities are the same (MSMEs and corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and PSUs), the TReDS could deal with both receivables factoring as well as reverse factoring so that higher transaction volumes come into the system and facilitate better pricing. 5. The transactions processed under TReDS will be “without recourse” to the MSMEs. Definitions 6. For the purpose of the Scheme, notwithstanding any other definition used in any other context, scheme, law or document, the following definitions are used: a) Factoring unit - a standard nomenclature used in the TReDS for an invoice or a bill on the system. Factoring Units may be created either by the MSME seller (in the case of factoring) or by corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and PSUs, (in case of reverse factoring) as the case may be. b) Financier – refers to banks, NBFC Factors and other financial institutions as permitted by the Reserve Bank of India participating in the TReDS and accepting the factoring unit for financing purpose. Participants 7. MSME sellers, corporate and other buyers, including the Government Departments and PSUs, and financiers (banks, NBFC Factors and other financial institutions as permitted by the Reserve Bank of India) will be direct participants in the TReDS. The TReDS will provide the platform to bring these participants together for facilitating uploading, accepting, discounting, trading and settlement of the invoices / bills of MSMEs. The bankers of sellers and buyers may be provided access to the system, where necessary, for obtaining information on the portfolio of discounted invoices / bills of respective clients. The TReDS may tie up with necessary technology providers, system integrators and entities providing dematerialisation services for providing its services. Process flow and procedure 8. The objective of the TReDS is to facilitate financing of invoices / bills of MSMEs drawn on corporate and other buyers, including the Government Departments and PSUs, by way of discounting by financiers. To enable this, the TReDS has to put in place suitable mechanism whereby the invoice / bill is converted into “factoring unit” as indicated in the Annex. 9. In the first phase, the TReDS would facilitate the discounting of these factoring units by the financiers resulting in flow of funds to the MSME with final payment of the factoring unit being made by the buyer to the financier on due date. In the second phase, the TReDS would enable further discounting / re-discounting of the discounted factoring units by the financiers, thus resulting in its assignment in favour of other financiers. 10. The process flow of the TReDS has to enable at the minimum, the uploading of invoices/bills and creation of factoring units by the MSME sellers; its acceptance by the corporate and other buyers, including the Government Departments and PSUs, within a specified time limit; discounting, rating and re-discounting of factoring units; sending of notifications at each stage to the relevant parties to the transaction; reporting and MIS requirements; and finally, generation and submission of settlement of obligations. In case of reverse factoring, the buyer could also create factoring units based on the documents uploaded by the MSME seller. A brief illustrative outline of the minimum features required in the process flow is given in the Annex. 11. The actual business, technical and operational processes and procedures to be followed in the system will be prepared by the entity operating the TReDS, and will be part of the Procedural Guidelines for the system. 12. The TReDS may also undertake some random audits to ensure that the factoring units uploaded on the exchange are authentic & based on genuine underlying transactions involving the sale of goods or services. 13. TReDS would put in place a standardized mechanism / process for on-boarding of buyers and sellers on the TReDS. This one-time on-boarding process will require the entities to submit all KYC related documents to the TReDS, along with resolutions / documents specific to authorised personnel of the buyer, and the MSME seller. Such authorised personnel would be provided with IDs / Passwords for TReDS authorisations (multi-level). Indemnity in favour of TReDS, if required, may also be given if it is made part of the standardized on-boarding process. 14. The KYC documentation and its process may be standardised and disclosed to all stakeholders by TReDS. As it requires confirmation of the banker of the MSME seller / buyer, as the case may be, the KYC documentation may be synchronous with the documentation / verification done by the banks in adherence to the extant regulatory requirements (Reserve Bank of India’s “Master Direction - Know Your Customer (KYC) Direction, 2016” dated February 25, 2016 (as amended from time to time)). 15. There would be a one-time agreement drawn up amongst the participants in the TReDS: a) Master agreement between the financier and the TReDS, stating the terms and conditions of dealings between both the entities. b) Master agreement between the buyers and the TReDS, stating the terms and conditions of dealings between both the entities. This agreement should clearly capture the following aspects:
c) Master agreement between the MSME sellers and the TReDS, stating the terms and conditions of dealings between both the entities. The agreement should also have a declaration / undertaking by the MSME seller that, in respect of goods and services underlying the factoring unit, no finance is extended by the working capital financing bank and such goods and services are not charged to the working capital financing bankers (i.e., finance availed through the TReDS would not be part of existing charge / hypothecation of its working capital bankers). d) In case of financing on the basis of invoices, an assignment agreement would need to be executed between the MSME seller and the financier. Alternatively, this aspect may be incorporated in the agreement between the MSME seller and the financier, to the effect that any financing transaction on TReDS will tantamount to an assignment of receivables in favour of whoever is the financier. e) The TReDS will be in custody of all the agreements. 16. Other procedural aspects of TReDS functioning and operations may be incorporated either in the Master Agreement, if so necessitated by the participants, or in the Procedural Guidelines where applicable. In all instances, such procedural aspects, even if incorporated in the Master Agreements, should be in adherence to regulatory norms issued from time to time. The Master Agreement may also clearly indicate that any legal proceedings to be initiated by one entity against another, if at all, will be outside the purview of TReDS. 17. TReDS will also review the need for CERSAI registration for the assignments as indicated above, and put in place a suitable mechanism for the same (preferably driven automatically through the TReDS), as soon as feasible after a factoring unit has been accepted for financing by a financier. Settlement process 18. Critical to the operations of the TReDS is the mechanism that ensures timely settlement of funds between the member financiers and the MSME sellers (when the factoring unit is financed) and the subsequent settlement of funds between the member buyers and the respective financiers on due date of the factoring unit. In order to ensure a smooth process of such payments, the TReDS would be required to: a) Trigger settlement between financier and MSME for accepted bids - In respect of all factoring units financed on a given day, the TReDS will generate the payment obligations of all financiers on T+2 basis and send the file for settlement in any of the existing payment system as agreed among the system participants. The TReDS would have to put in place a separate recourse mechanism to handle settlement failures in respective payment systems. b) Trigger settlement between the buyer and the ultimate financier on due date - the TReDS would generate the payment obligations file and send the same for settlement on due date to the relevant payment system. 19. The TReDS will generate the settlement files and send the same to existing payment systems for actual payment of funds. This would ensure that the inter-bank settlement (between the bankers representing member MSMEs, buyers and the financiers) will take place and defaults, if any, by the buyers will be handled by the buyer’s bank and will not be the responsibility of the TReDS. Hence, the settlement process ensures payments to relevant recipients on due date, thus, facilitating the smooth operations on the TReDS. However, it would not entail a guaranteed settlement by the TReDS. 20. The TReDS would be required to put in place a mechanism for bankers to report defaults in payments by buyers. The TReDS would also need to ensure adequate arbitration and grievances redressal mechanism is in place. Regulatory framework for TReDS 21. The TReDS, which undertakes clearing and settlement activities, would be governed by the regulatory framework put in place by the Reserve Bank of India under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act 2007 (PSS Act). It will function as an authorised payment system under the PSS Act 2007. The activities of the TReDS as well as those of the participants in the TReDS would be governed by the relevant legal and regulatory provisions applicable to various stakeholders in the system. As such, the processes and procedures of the TReDS should be compliant with such legal and regulatory provisions which may be issued and amended from time to time by respective authorities. Eligibility criteria to set up and operate the TReDS 22. Entities desirous of setting up and operating the TReDS should fulfil the following criteria. (a) Financial Criteria (i) Since the TReDS will not be allowed to assume any credit risk, its minimum paid up equity capital shall be Rs. 25 crore. (ii) The foreign shareholding in the TReDS would be as per the extant foreign investment policy. (iii) Entities, other than the promoters, will not be permitted to have shareholding in excess of 10 per cent of the equity capital of the TReDS. (iv) The overall financial strength of the promoters/entity seeking to set up TReDS would be an important criteria of assessment/selection. (b) Due diligence of promoters The entities and their promoters/promoter groups as defined in the SEBI (Issue of Capital & Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2009 should be ‘fit and proper’ in order to be eligible to operate as TReDS. RBI would assess the ‘fit and proper’ status of the applicants on the basis of their past record of sound credentials and integrity; financial soundness and track record of at least 5 years in running their businesses. RBI may, inter alia, seek feedback on the applicants on these or any other relevant aspects from other regulators, and enforcement and investigative agencies like Income Tax, CBI, Enforcement Directorate, SEBI, etc. as deemed appropriate. (c) Technological capability The TReDS should have sound technological basis to support its operations. As such, the TReDS should, at the minimum, fulfil the following technological requirements.
Application procedure for Authorisation 23. The general guidelines as well as the application format for any non-bank entity to seek authorisation under the PSS Act for operating a payment system are available at /documents/87730/21647585/86707.pdf 24. Entities meeting the eligibility criteria as outlined in the Guidelines and desirous of setting up the TReDS, may apply in the prescribed format to the Chief General Manager, Department of Payment and Settlement Systems, Reserve Bank of India, 14th Floor, Central Office Building, Shaheed Bhagat Singh Marg, Mumbai – 400001, as and when the window for receipt of applications for this purpose is opened. Illustrative Outline of Process flow under TReDS a) Corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and Public Sector Undertakings, send purchase order to MSME seller (outside the purview of the TReDS). b) MSME seller delivers the goods along with an invoice. There may or may not be an accepted bill of exchange depending on the trade practice between the buyer and the seller (outside the purview of the TReDS). c) Thereafter, on the basis of either an invoice or a bill of exchange, the MSME seller creates a ‘factoring unit’ (which would be a standard nomenclature used in the TReDS for an invoice or a bill on the system) on TReDS. Subsequently, the buyer also logs on to TReDS and flags this factoring unit as ‘accepted’. In case of reverse factoring, this process of creation of factoring unit could be initiated by the buyer. d) Supporting documents evidencing movement of goods etc. may also be hosted by the MSME seller on the TReDS in accordance with the standard list or check-list of acceptable documents indicated in the TReDS. e) The TReDS will standardise the time window available for buyers to ‘accept’ the factoring units, which may vary based on the underlying document – an invoice or bill of exchange. f) The TReDS may have either a single or two separate modules for transactions with invoices and transactions with Bills of Exchange, if so required. In either case, all transactions routed through TReDS will, in effect, deal with factoring units irrespective of whether they represent an invoice or a bill of exchange. g) Factoring units may be created in each module as required. Each such unit will have the same sanctity and enforceability as allowed for physical instruments under the “Factoring Regulation Act, 2011” or under the “Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881” h) The standard format / features of the ‘factoring unit’ will be decided by the TReDS – it could be the entire bill/invoice amount or an amount after adjustment of tax / interest etc. as per existing market practice and as adopted as part of the TReDS procedure. However, each factoring unit will represent a confirmed obligation of the corporate and other buyers, including Government Departments and PSUs, and will carry the following relevant details – details of the seller and the buyer, issue date (could be the date of acceptance), due date, tenor (due date – issue date), balance tenor (due date – current date), amount due, unique identification number generated by the TReDS, account details of seller for financier’s reference (for credit at the time of financing), account details of buyer for financier’s reference (for debit on the due date), the underlying commodity (or service if enabled). i) The TReDS should be able to facilitate filtering of factoring units (by financiers or respective sellers / buyers) on any of the above parameters. In view of the expected high volumes to be processed under TReDS, this would provide the necessary flexibility of operations to the stakeholders. j) The buyer’s bank and account details form an integral feature of the factoring unit. The creation of a factoring unit on TReDS shall result in automatic generation of a notice / advice to the buyer’s bank informing them of such units. k) These factoring units will be available for financing by any of the financiers registered on the system. The all-in-cost quoted by the financier will be available on the TReDS. This price can only be viewed by the MSME seller and not available for other financiers. l) There will be a window period provided for financiers to quote their bids against factoring units. Financiers will be free to determine the time-validity of their bid price. Once accepted by the MSME seller, there will be no option for financiers to revise their bids quoted online. m) The MSME seller is free to accept any of the bids and the financier will receive the necessary intimation. Financiers will finance the balance tenor on the factoring unit. n) Once a bid is accepted, the factoring unit will get tagged as “financed” and the funds will be credited to the seller’s account by the financier on T+2 basis (T being the date of bid acceptance). The actual settlement of such funds will be as outlined under the Settlement section. o) Once an accepted factoring unit has been financed by a financier, notice would be sent to buyer’s bank as well as seller’s bank. While the buyer’s bank would use this information to ensure availability of funds and also handle the direct debit to the buyer’s account on the due date in favour of the financier (based on the settlement obligations generated by the TReDS), the seller’s bank will use this input to adjust against the working capital of the MSME seller, as necessary (the TReDS procedures may, if necessary, also indicate that the proceeds of the accepted and financed factoring units will be remitted to the existing working capital / cash credit account of the MSME seller). If agreed by members, the TReDS may also provide the option to members, whereby the financiers would take direct exposure against the buyers rather than through their bankers. p) On the due date, the financier will have to receive funds from the buyer. The TReDS will send due notifications to the buyers and their banks advising them of payments due. The actual settlement of such funds will be as outlined under the Settlement section. q) Non-payment by the buyer on the due date to their banker should tantamount to a default by the buyer (and be reported as such as per regulatory procedures prescribed from time to time) and enable the banker to proceed against the buyer. Any action initiated in this regard, will be strictly non-recourse with respect to the MSME sellers and outside the purview of the TReDS. r) These instruments may be rated by the TReDS on the basis of external rating of the buyer, its credit history, the nature of the underlying instrument (invoice or bill of exchange), previous instances of delays or defaults by the buyer with respect to transactions on TReDS, etc. s) The rated instruments may then be further transacted / discounted amongst the financiers in the secondary segment. t) Similar to the primary segment, any successful trade in the secondary segment will also automatically result in a direct debit authority being enabled by the buyer’s bank in favour of the financier (based on the settlement obligations generated by the TReDS). In parallel, it will also generate a ‘notice of assignment’ intimating the buyer to make the payment to the new financier. u) In the event that a factoring unit remains unfinanced, the buyer will pay the MSME seller outside of the TReDS. In order to meet the requirements of various stakeholders, the TReDS should ensure to provide various types of MIS reports including intimation of total receivables position, financed and unfinanced (to sellers); intimation of outstanding position, financed and unfinanced with details of beneficiaries and beneficiary accounts to be credited (for buyers); total financed position for financiers; etc. Similarly, data on unfinanced factoring units in the market should also be made available by the TReDS. The system should also generate due date reminders to relevant parties, notifications to be issued to bankers when a factoring unit is financed, notifications to be issued to buyers once a factoring unit related to their transaction is traded in the secondary segment, etc. |
ಪೇಜ್ ಕೊನೆಯದಾಗಿ ಅಪ್ಡೇಟ್ ಆದ ದಿನಾಂಕ:













